GitLab Sensor User Guide
The GitLab Sensor integrates GitLab (cloud or self-hosted) with Keyfactor's AgileSec Platform. It allows you to discover, inventory, and analyze cryptographic assets across multiple repositories within a GitLab organization or group.
Overview
Key Features
Organization-Wide Scanning: Scan all repositories in a GitLab group or organization in a single execution.
Flexible Filtering: Use glob patterns (including
**globbing) to include or exclude specific repositories.Deep Cryptographic Discovery: Automatically identifies certificates, private keys, keystores, and cryptographic libraries embedded in source code.
Incremental Scanning: Efficiently scans only new or modified files in subsequent runs.
Cloud and Self-Hosted Support: Works with GitLab.com and self-hosted GitLab instances.
What Gets Scanned
The sensor downloads repository archives from GitLab and analyzes all files to discover:
X.509 Certificates: SSL/TLS certificates, code signing certificates, client authentication certificates
Private Keys: RSA, DSA, EC private keys in PEM, DER, and PKCS8 formats
Java Keystores: JKS, JCEKS, PKCS12 keystores
Tokens: JWT and JWE tokens
Cryptographic Libraries: OpenSSL, BouncyCastle, cryptography.io, and other crypto implementations
Container Images: Certificates and keys embedded in Docker/OCI images
Code Artifacts: Embedded certificates in compiled code (JAR, WAR, EAR files)
Source Code: Use of cryptographic algorithms and libraries in source code
Prerequisites
GitLab Requirements
Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
Protocol | HTTPS required for API access. |
Access | Network connectivity from the sensor machine to the GitLab server. |
API Access | GitLab API v4 must be accessible. |
Token | Personal Access Token with |
Supported Authentication Methods
The Gitlab sensor supports token-based authentication
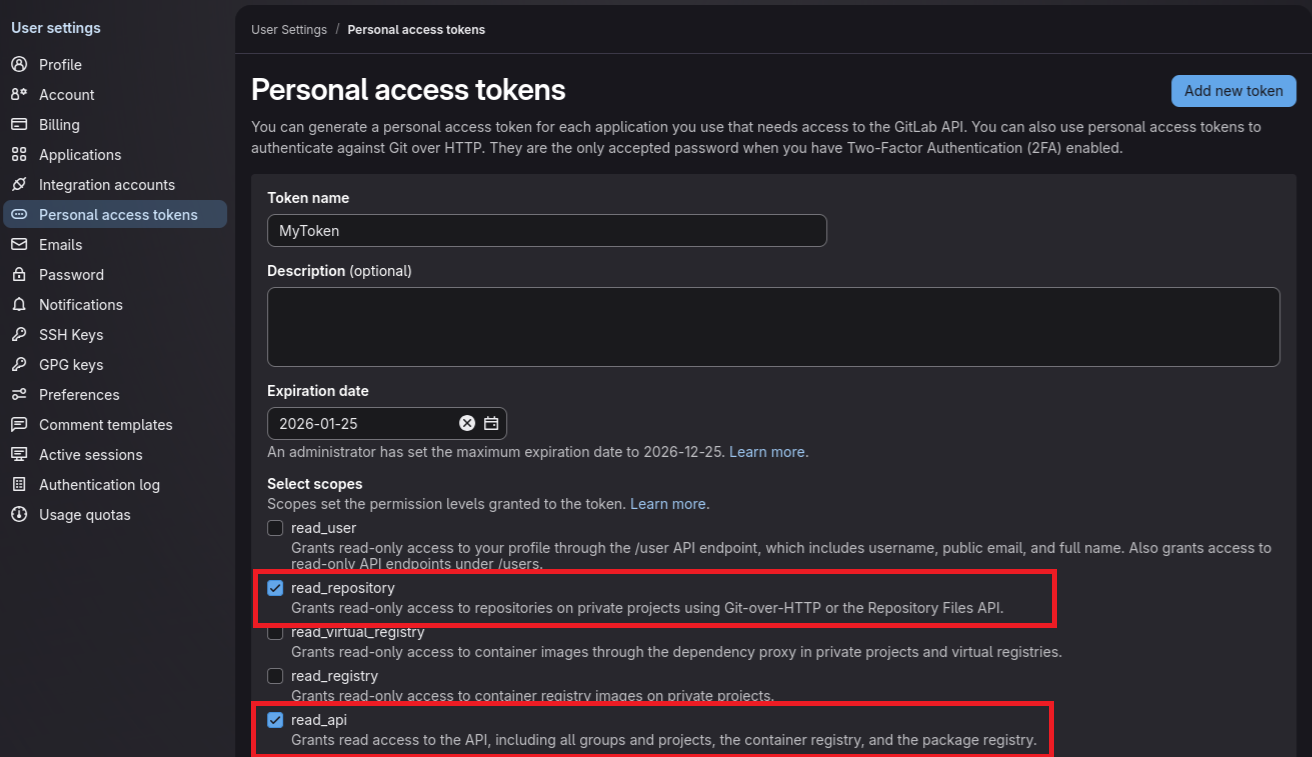
Step 1: Generate a Personal Access Token
Log in to GitLab
Go to User Settings → Access Tokens (or navigate to
https://gitlab.com/-/user_settings/personal_access_tokens)Create a new token with the following scopes: -
read_api— Required for listing repositories -read_repository— Required for downloading repository archivesCopy the token immediately — it will only be shown once
Store the token securely
Step 2: Verify Token
Test the token to ensure it works:
CODE# set your token export GITLAB_TOKEN="your-token-here" export GITLAB_URL="https://gitlab.com" # or your self-hosted URL # test authentication curl -H "PRIVATE-TOKEN: ${GITLAB_TOKEN}" \ "${GITLAB_URL}/api/v4/projects?per_page=1" # expected: json array with project info
Required Access Rights
The GitLab access token must have the following permissions to successfully authenticate:
Permission | Purpose | Required |
|---|---|---|
read_api | required for downloading repository | ✅ Yes |
read_repository | required for enumerating repositories | ✅ Yes |
Running the Sensor
The sensor can be executed from the Platform UI, through the Scan API, or remotely using the Unified Sensor CLI.
Run from the Platform UI
Refer to Sensors Architecture and Overview for additional details on how to configure sensor through UI.
Platform Scan Configuration
Step 1: Navigate to the Sensor Setup page: Scan → Sensors → Choose a Sensor → Git Sensor
Step 2: Configure the sensor parameters.
Fill in the required configuration parameters:
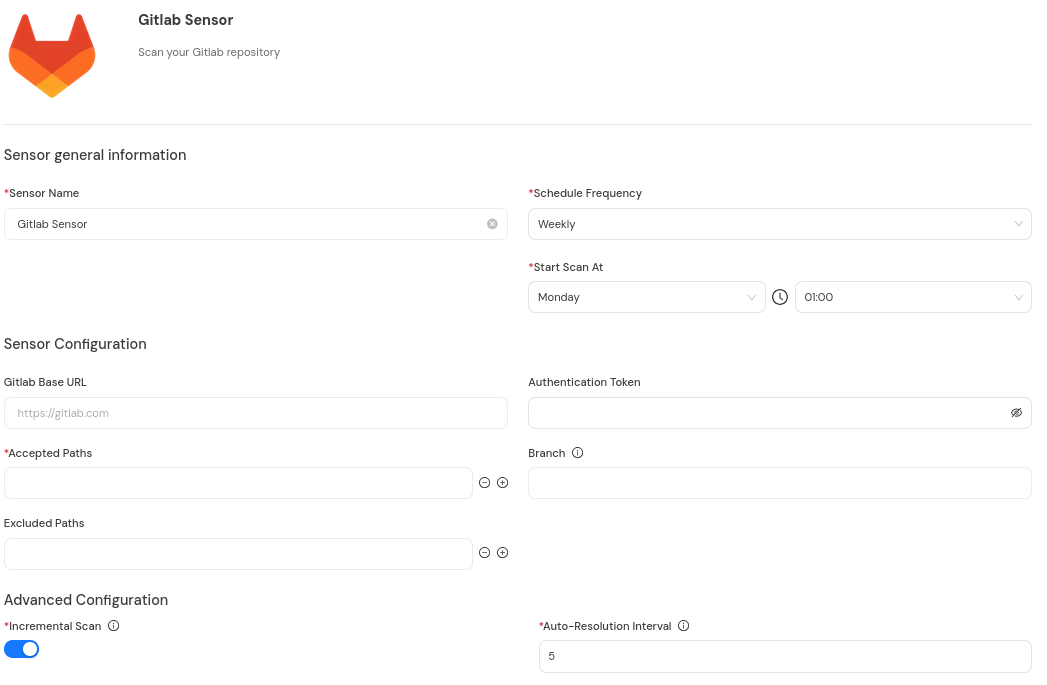
Platform Scan Configuration Fields
Field Name | Display Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gitlab Base URL | Single-line text | ❌ No | Only specify this field if self-hosting a GitLab instance. For http://GitLab.com , leave blank (defaults to https://gitlab.com ). For self-hosted instances, use your GitLab URL (e.g., https://gitlab.company.com) |
| Authentication Token | Password field | ❌ No | Required for scanning private repos. Requires |
| Branch | Single-line text | ❌ No | Branch to scan (if not specified, default branch is inferred) |
| Accepted Paths | Multiple values | ✅ Yes | Glob patterns for repositories to include in group/subgroup/project format (e.g., gitlab-org/** for all projects in a group including subgroups, or gitlab-org/charts/gitlab for a specific project). |
| Excluded Paths | Multiple values | ❌ No | Glob patterns for repositories to exclude from the included set, in group/subgroup/project format (e.g., gitlab-org/archived-*). |
| Incremental Scan | Boolean | ✅ Yes | Enable to scan only updates since last run, see Sensors Architecture and Overview - Incremental Scanning |
| Auto-Resolution Interval | Number | ✅ Yes | Number of incremental scans to perform before running a full scan, see Sensors Architecture and Overview - Incremental Scanning |
Scan Execution Using API
For complete field definitions, supported parameters, and error handling details, see Scan API.
Request Body
The complete request body contains sensor configuration in the sensorConfig field, i.e:
{
"sensorName": "<sensor name>",
"sensorType": "Gitlab Sensor",
"sensorConfig": {
"url": "<gitlab api url>",
"branch": "<branch name>",
"token": "<personal access token>",
"include_paths": "<include patterns>",
"exclude_paths": "<exclude patterns>"
},
"callbackId": "<callback id>",
"labels": [
{
"<label name>": "<label value>"
}
],
"priority": "<priority>",
"incrementalScan": true,
"autoResolutionInterval": 5
}
API Field Descriptions
For API fields and descriptions, see Scan API.
Run Remotely (Unified Sensor CLI)
Use following config for running sensor through the unified sensor CLI:
Scan All Repos in an Org (Public)
CODEscan_config: plugins: - isg_gitlab - trigger_discover - export config: isg_gitlab: plugin_config: include_paths: - "myorg" # Equivalent to "myorg/**"Self-Hosted GitLab (With Auth)
CODEscan_config: plugins: - isg_gitlab - trigger_discover - export config: isg_gitlab: plugin_config: url: "https://git.mycompany.com" token: "${env:GITLAB_TOKEN}" include_paths: - "internal-team/**" exclude_paths: - "internal-team/archived-*"Scan Specific Branch
CODEscan_config: plugins: - isg_gitlab - trigger_discover - export config: isg_gitlab: plugin_config: url: "https://gitlab.com" token: "${env:GITLAB_TOKEN}" branch: "develop" include_paths: - "myorg/myrepo"
The remote sensor contains an example configuration file in the directory config/sample-configs/gitlab.yml.
Known Limitations
Rate Limiting
Description: Gitlab enforces API rate limits.
Impact: Large organizations with many repositories may hit rate limits.
Workaround: For individual repositories you can use the Git Sensor.
Binary Files
Description: While the sensor scans files, opaque binary blobs without recognized headers may not be deeply analyzed.
Troubleshooting
Common Errors
401 UnauthorizedCause: Invalid or expired Personal Access Token.
Fix: Verify the token is correct and has not expired. Regenerate if necessary.
403 ForbiddenCause: Token lacks required scopes (
read_api,read_repository).Fix: Generate a new token with the correct scopes.
404 Not FoundCause: Repository or group does not exist, or token doesn't have access.
Fix: Verify the include patterns are correct and the token has access to the target repositories.
unable to access(Connection Refused)Cause: Network connectivity issue.
Fix: Ensure the machine running the sensor can reach the GitLab server URL. Check firewalls and proxies.
could not find remote branchCause: The specified branch does not exist on the remote.
Fix: Verify the branch name matches exactly (case-sensitive), or leave blank to use the default branch.
Getting Support
Collect diagnostic information:
Sensor version
Configuration file (redact tokens)
Log output
GitLab details (cloud vs self-hosted, URL, version)
.png)