Microsoft Auto-enrollment Overview
ENTERPRISE
The following provides an overview of Microsoft Auto-enrollment and support in EJBCA.
For guide and instructions on how to set up auto-enrollment, see Microsoft Auto-enrollment Operations.
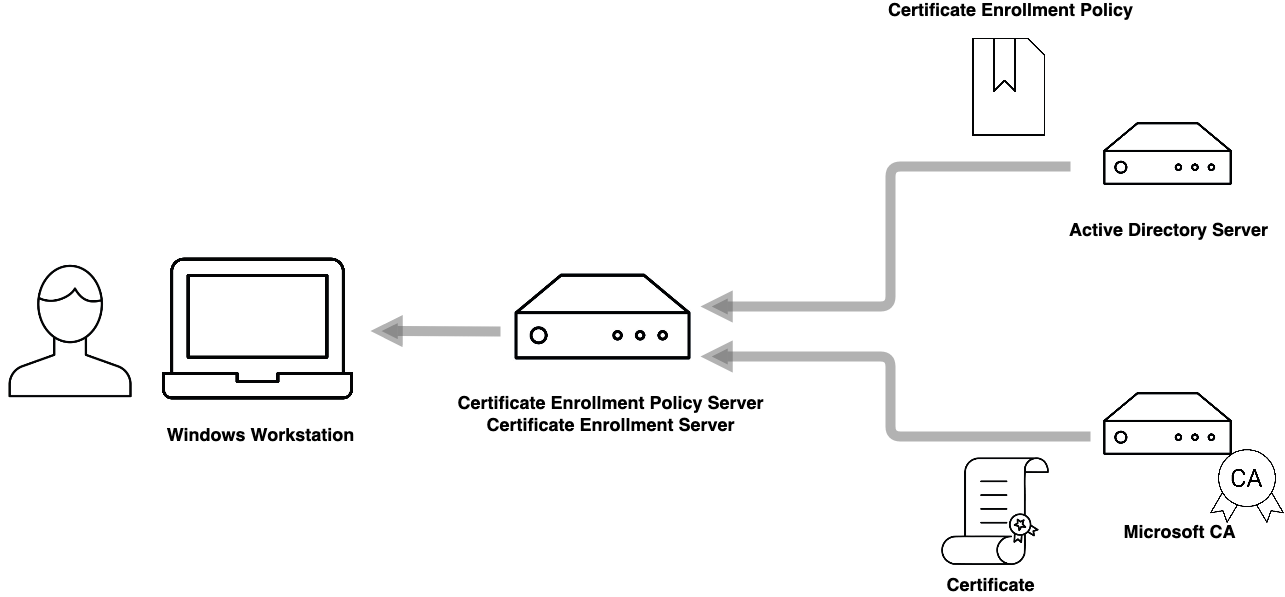
Auto-enrollment is the method with which Microsoft Windows servers and clients provision Active Directory (AD) certificates within a Microsoft domain. Once set up in Group Policy, clients connect to a configured Certificate Enrollment Policy Server (CEP), which initially returns a set of Certificate Enrollment Policies which entitles the client to the corresponding certificates. The client then sends a request for those certificates, which is passed on to a server running Microsoft CA, which enrolls the client for the requested certificates. This process is fully oblique to the client, as are any following certificate renewals. MSAE allows Windows administrators to maintain a PKI within their domains without requiring any action from users.
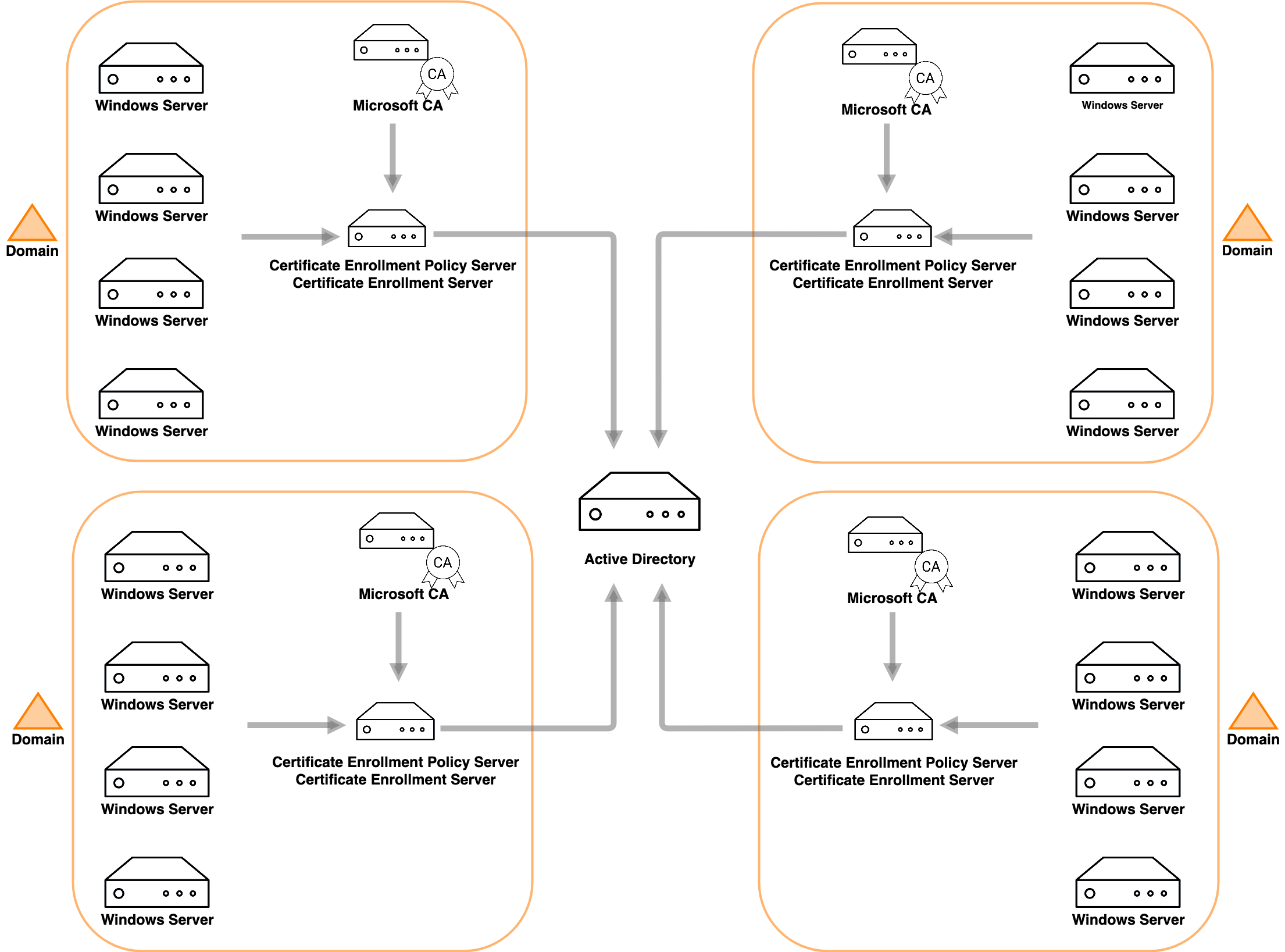
The problem with this setup is that it is domain specific. In other words, this setup needs to be duplicated for each domain you have in your organization. In an enterprise environment involving hundreds of domains and tens of thousands of users, this solution does not scale.
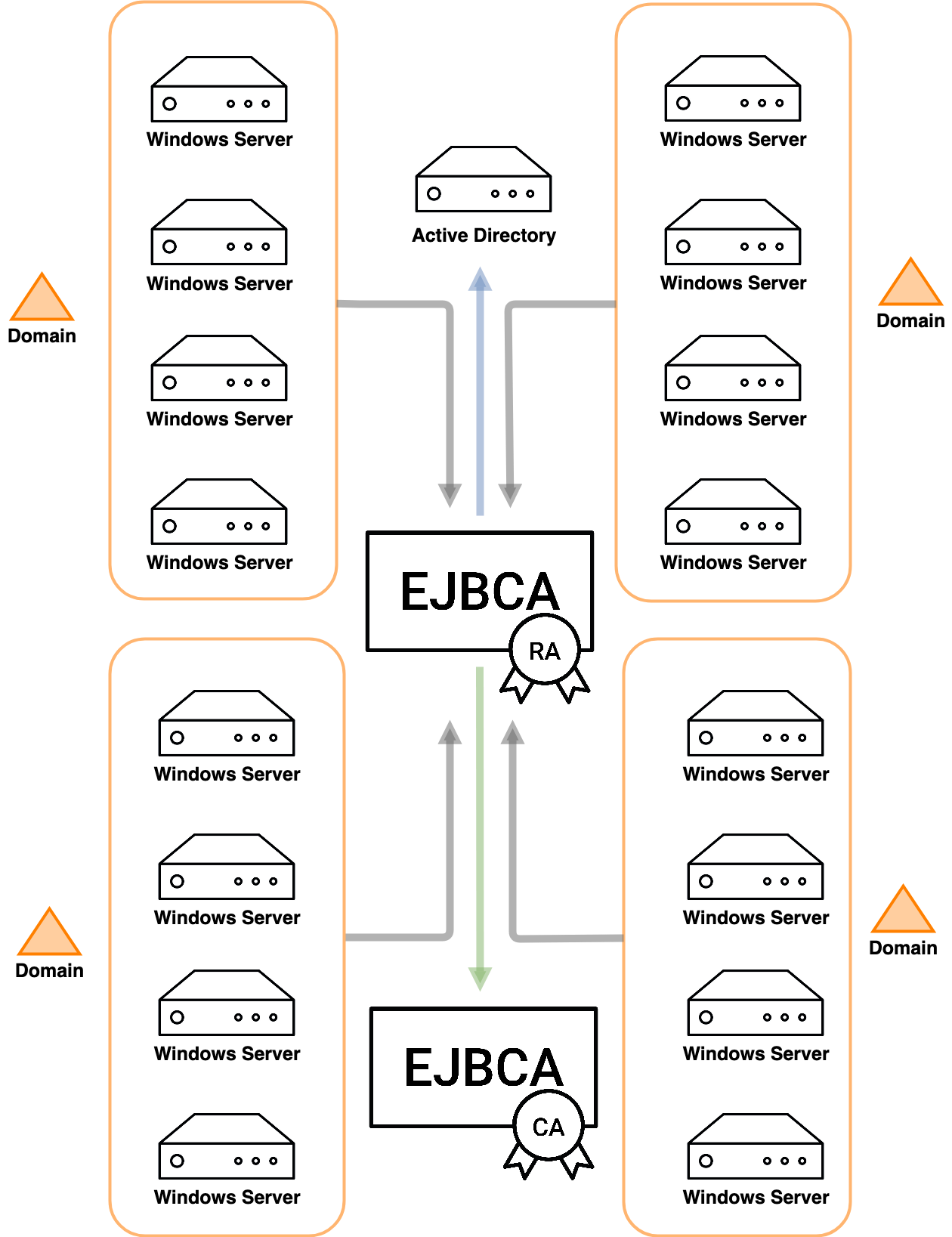
This is where EJBCA becomes your solution - by using the EJBCA CA instead of the Microsoft CA and configure the client to connect directly to EJBCA RA machines instead of a Microsoft Certificate Services, a single EJBCA CA can serve your entire Microsoft PKI through RA instances.
Microsoft Auto-enrollment Key Archival
As of 8.2, EJBCA supports key archival and recovery for Microsoft auto-enrollment. By default, EJBCA stores encrypted keys in the database and enables administrators to retrieve keys in case a private key is lost. Microsoft auto-enrollment key archival is configured in the Windows server certificate template and in EJBCA's system configuration, auto-enrollment alias, and end entity. For more information on how to configure auto-enrollment in EJBCA, see Microsoft Auto Enrollment Configuration, and for more information about how to recover the private key, see Key Archival: Recovery.
Only RSA keys are supported for archival and recovery.
To enhance security, a CA Administrator role can be assigned for key recovery and a CA Administrator can for example be configured to have the capability to recover a key for a specific end entity profile only. For more information on how to create a CA Administrator role, see Roles and Access Rules Operations. Additionally, you can configure an approval mechanism to ensure that a key recovery is approved by several administrators. EJBCA provides two types of approval profiles, Accumulative and Partitioned, see Approvals.
.png)