Remote Authenticators Overview
The following provides information about the concepts of Remote Authenticators (Internal Keybindings).
For more information about how to manage Remote Authenticators, see Managing Remote Authenticators.
Note that prior to EJBCA 7.11.0, Remote Systems were known as Authentication Keybindings.
Overview
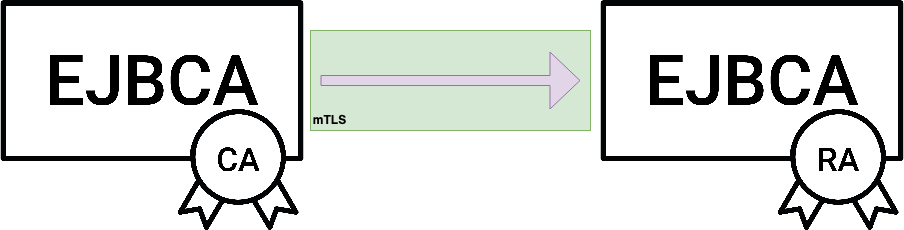
When EJBCA connects to another node running EJBCA (e.g. a CA connecting to a VA or RA) it does so over the Peers Protocol, which uses mTLS and is always initiated by the CA.
The server-side authentication (from the RA) is handled through standard TLS measures, but for mTLS the client (the CA) has to provide authentication as well. The Remote Authenticator object provides a wrapper for a crypto token (containing a client-side TLS key) that can be signed by a CA known to the RA.
A Remote Authenticator can be used to make keys in a Crypto Token available for other uses than in a CA. It is a reference to a key pair available to the EJBCA instance, a non-CA certificate, an optional list of trusted certificates and properties for its purpose. It can be thought of as a simplified key store with purpose-specific properties. Once created and signed, the Remote Authenticator can be chosen in a Peer Connector to authenticate the connection.
Certificate Constraints
When issuing a certificate for a Remote Authenticator, the following constraints must be fulfilled:
- The certificate must have Key Usage: Digital Signature. The certificate should also have Key Usage: Key Encipherment if the key is an RSA key.
- The certificate must have Extended Key Usage: Client Authentication.
Configuration
The following provides an overview of the configuration. For a step-by-step example, see Setting up a Remote Authenticator.
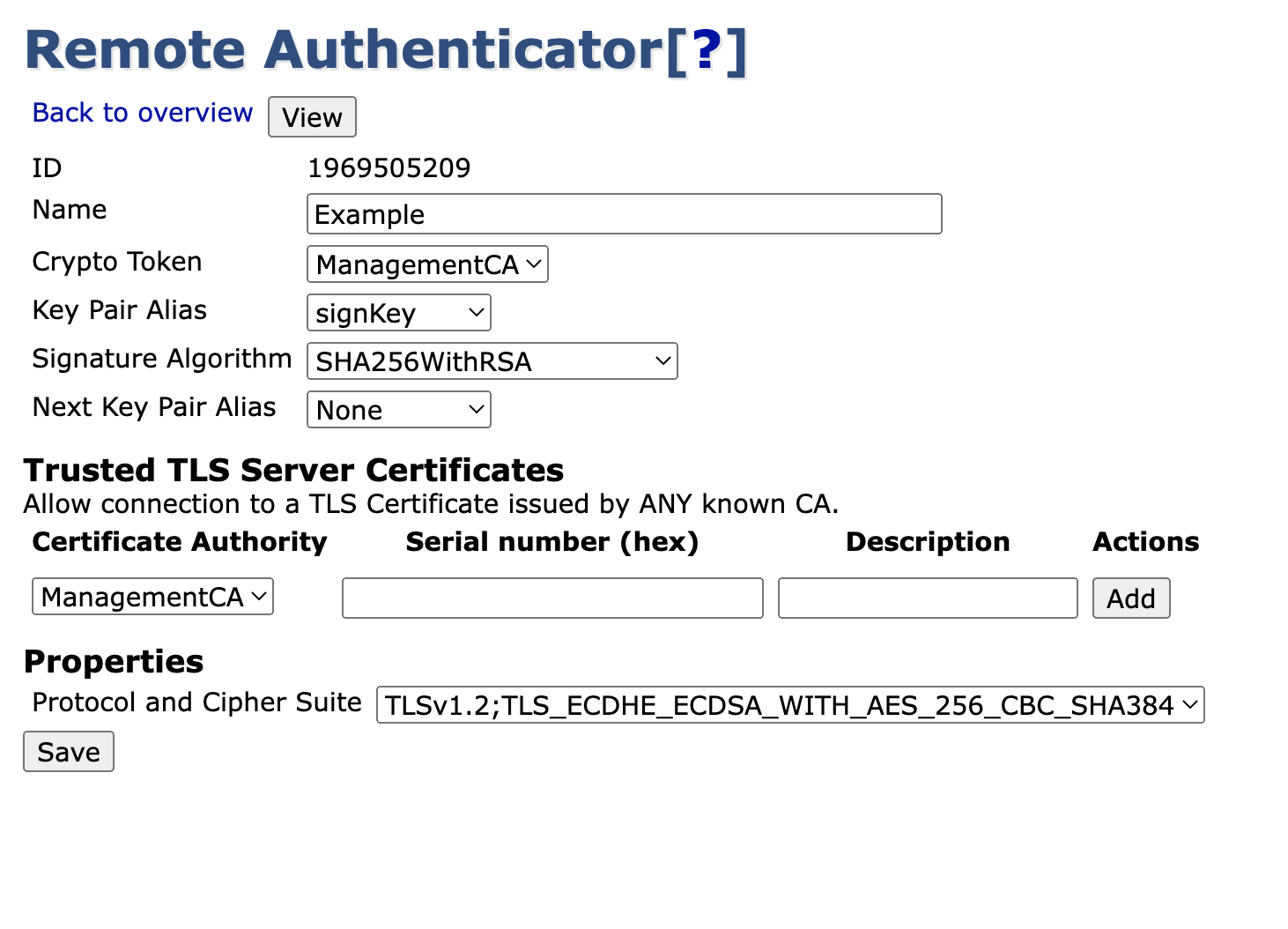
Common Settings
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Id | Unique identifying number. |
Name | A unique and human readable name. |
Crypto Token | The Crypto Token where we reference a key pair. |
Key Pair Alias | A reference to the currently used key pair in the specified Crypto Token. |
Signature Algorithm | The signature algorithm user during signing, for example the signing of an OCSP response. |
Next Key Pair Alias | A reference to the next key pair to use in the specified Crypto Token when renewing. |
Trusted Server Certificates
The Remote Authenticator can be constrained to a limited subset of servers to be able to connect to.
- By default, any remote server-side TLS certificate issued by a CA that exists in the local EJBCA instance will be trusted.
- By specifying a CA, you can choose to trust only TLS certificates issued by this CA.
- By specifying both a CA and a certificate serial number, only the specific TLS certificate will be trusted.
Protocol And Cipher Suite
The Authentication Key Binding defines a protocol and a cipher suite to use for the outgoing TLS connection. The protocols and cipher suites accessible in EJBCA are configured in cesecore.properties.
To add additional protocols and cipher suites, do the following:
- Copy
cesecore.properties.samplefrom EJBCA'sconfdirectory and use it as a template. Ifallow.external-dynamic.configurationis enabled, you can override the default configuration by putting thecesecore.propertiesconfiguration file in/etc/cesecore/conf. Edit
cesecore.propertiesand look for the Authentication Key Binding settings. Specify the supported protocols and cipher suites using theauthkeybind.ciphersuiteproperty. For example:CODEauthkeybind.ciphersuite.0=TLSv1.2;TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 authkeybind.ciphersuite.1=TLSv1.2;TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256A complete list of all available protocols and cipher suites to choose from is available in the Java Cryptography Architecture Oracle Providers Documentation for JDK 8 or the corresponding document for your JDK distribution.
- If
allow.external-dynamic.configurationis enabled it should be sufficient to restart the application server for the changes to take effect. Otherwise, you need to recompile and redeploy EJBCA.
.png)