Tutorial - Deploy Istio Service Mesh in a Multi-Cluster Kubernetes Environment Using EJBCA as an External PKI provider
In this tutorial, you will learn how to set up Istio in a multi-cluster Kubernetes environment using EJBCA as an external CA. The multi-cluster setup with Istio and EJBCA allows a scalable and high-availability Kubernetes environment with full PKI functionality. Istio will be set up on a primary cluster and a remote cluster will be configured to use the primary one.
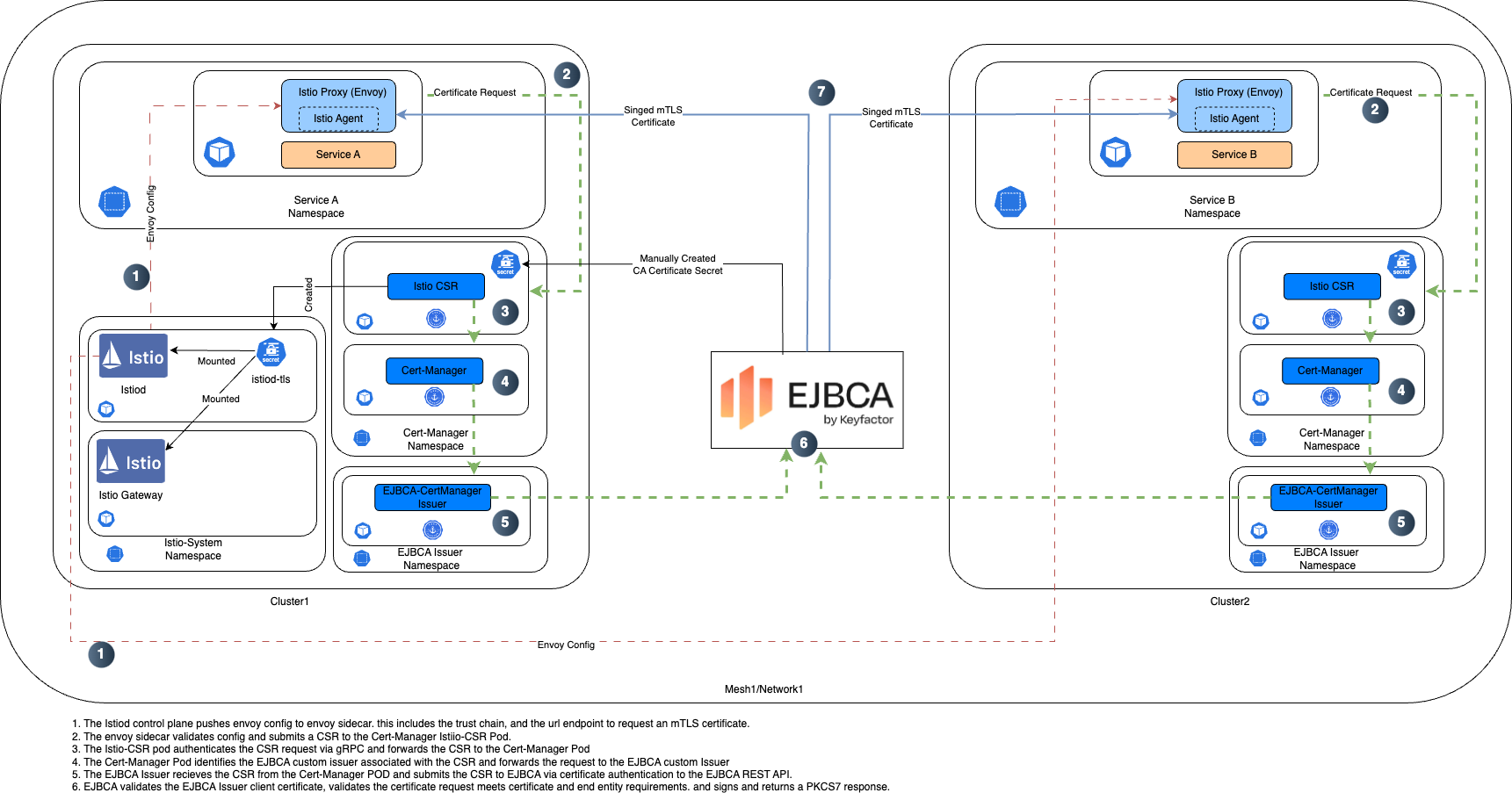
The following illustrates a typical architecture:
The tutorial covers these steps:
Required Prerequisites
EJBCA Preparation
Primary cluster configuration and setup
Secondary cluster configuration and setup
Prerequisites
For this tutorial, EJBCA Community container version 8.3.2 was used.
Before you begin, you need:
Two Virtual Machines (VMs) on the same network with MicroK8s installed on each VM. Refer to MicroK8s - Get started to install MicroK8s. One MicroK8s instance will be used as a Primary K8s instance and the other will be the Remote K8s instance.
Istioctl installed on each MicroK8s VM. Refer to Download the Istio release to install istioctl
Istio source files downloaded to each MicroK8s VM. Download using Git from Istio’s GitHub page GetHub - Istio: Connect, secure, control, and observe services. Note that this is covered in step Install Istio Gateway below.
Helm installed on each MicroK8s VM. Refer to Helm - Installing Helm to install.
Step 1 - EJBCA Preparation
In this step, you will create the client certificates used to connect to the EJBCA REST API. You will also export the CA certificates from EJBCA so that they can be used to define trust throughout this deployment. This tutorial will use the equivalent of a SuperAdmin certificate. However, it should be noted that you can create a role to isolate permissions of the client certificate used to connect to EJBCA. Additionally, you will be utilizing the Management CA since this CA was used to create the TLS Certificate used by EJBCA for the Web and REST API interfaces.
Issue client certificate
To issue a client certificate in EJBCA RA, follow these steps:
In EJBCA, click RA Web and select Make New Request.
For Certificate Type, select the Admin End Entity Profile.
For Key-pair generation, select By the CA.
Specify the following information about the holder of the certificate, to be used in the certificate:
For CN, Common Name, specify a name, in this example EJBCA-Issuer.
For Username, add EJBCA-Issuer. The Username is the name that will go into the database and is often the same as the Common Name.
For Enrollment code: Enter a password twice. This password will be used to encrypt the certificate bundle (P12 file) once downloaded.
Click Download PKCS#12 to download and save the PKCS#12 certificate.
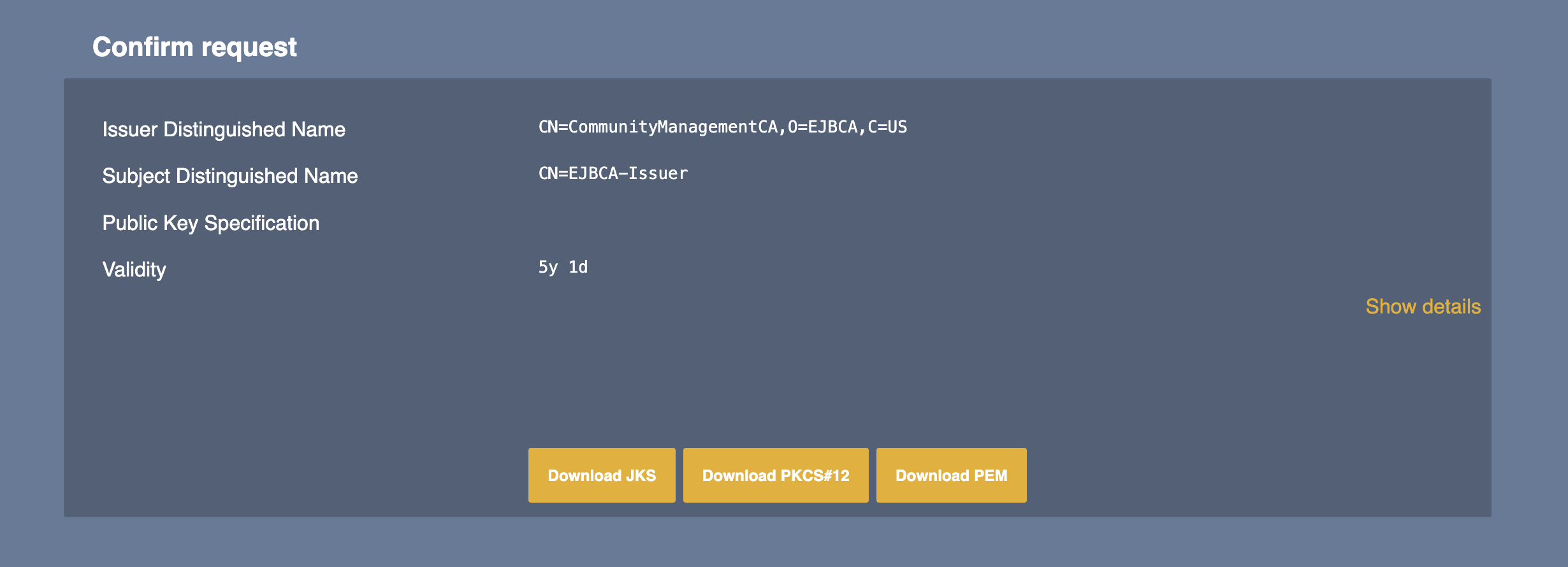
The client certificate is downloaded as a ejbca-issuer.p12 file.
Extract public and private key files
Next, extract the PKCS12 into separate base64 public and private key files.
In a command shell, navigate to the directory containing the ejbca-issuer.p12 file and run the following command to extract the private key to a separate private key file.
openssl pkcs12 -in ejbca-issuer.p12 -nocerts -out ejbca-issuer.key -nodesThe command above will prompt you for the password that was used for the enrollment code in an earlier step.
openssl pkcs12 -in ejbca-issuer.p12 -nocerts -out ejbca-issuer.key -nodes
Enter Import Password:Next, extract the public key, by running the following command.
openssl pkcs12 -in ejbca-issuer.p12 -nokeys -out ejbca-issuer.pemThe command above will prompt you for the password that was used for the enrollment code in an earlier step.
openssl pkcs12 -in ejbca-issuer.p12 -nokeys -out ejbca-issuer.pem
Enter Import Password:Download CA certificate
Next, download the CA certificate used to create the ejbca-issuer client certificate. The CA certificate will be saved to a PEM file and used later as a trust store for all Cert-Manager and Istio components.
In RA Web, click CA Certificates and CRLs in the menu bar.
On the CA Certificates and CRLs page, for the Management CA, click PEM in the Certificate column.
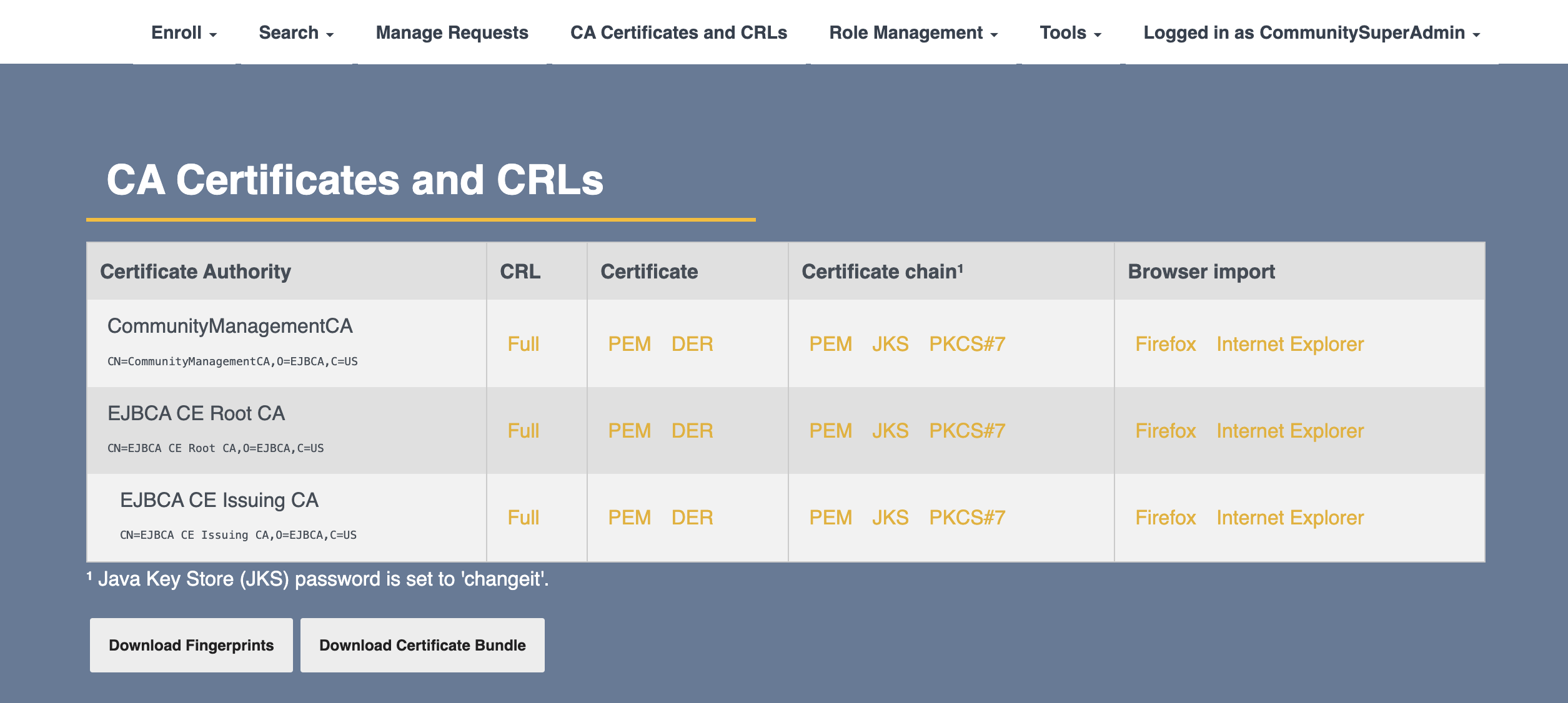
The CA certificate is downloaded in base64 PEM format
The CA certificate ManagementCA.pem file is now downloaded.
Step 2 - Deploy Primary Cluster
In this section, you will learn how to configure the primary MicroK8s VM as the Istio Primary instance. As part of this procedure, you will install Cert-Manager, Cert-Manager Istio-CSR, Keyfactor EJBCA Cert-Manager Issuer, and Istio.
Add required repositories
First, add all the required repositories to the Primary MicroK8s VM.
To add the Helm repos:
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm repo add istio https://istio-release.storage.googleapis.com/charts
helm repo add ejbca-issuer https://keyfactor.github.io/ejbca-cert-manager-issuer
helm repo updateDeploy cert-manager tools
This section covers how to install Cert-Manager, Keyfactor EJBCA Cert-Manager Issuer, and the Cert-Manager Istio CSR Plugin for Cert-Manager on the Primary Cluster.
Install Cert-Manager via Helm:
helm install \
cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \
--namespace cert-manager \
--create-namespace \
--set crds.enabled=trueInstall EJBCA Cert-Manager custom issuer:
helm install ejbca-cert-manager-issuer ejbca-issuer/ejbca-cert-manager-issuer \
--namespace ejbca-issuer-system \
--create-namespaceCreate ejbca-secret by using ejbca-issuer certificate and key files that was created in Step 1 - EJBCA Preparation.
kubectl -n ejbca-issuer-system create secret tls ejbca-client-secret --cert=ejbca-issuer.pem --key=ejbca-issuer.keyCreate an ejbca-ca-secret using the Management CA certificate that was created Step 1 - EJBCA Preparation.
kubectl -n ejbca-issuer-system create secret generic ejbca-ca-secret --from-file=<ManagementCA-File>.pemCreate istio-system namespace.
kubectl create ns istio-systemCreate ejbca-cert-manager-issuer and apply it to the cluster.
You will need to update some of the values below to match your environment.
cat > issuer-ephemeralCA-spiffe-istio-system.yaml <<EOF
apiVersion: ejbca-issuer.keyfactor.com/v1alpha1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
namespace: istio-system
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: issuer
app.kubernetes.io/instance: istio-system-spiffe
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ejbca-issuer
app.kubernetes.io/created-by: ejbca-issuer
name: istio-system-spiffe
spec:
hostname: "<insert-ejbca-fqdn-here>"
ejbcaSecretName: "ejbca-client-secret"
certificateAuthorityName: "<insert-management-ca-name-here>"
certificateProfileName: "<insert-mtls-certificate-profile-name-here>"
endEntityProfileName: "<insert-mtls-certificate-profile-name-here>"
caBundleSecretName: ejbca-ca-secret
EOF
kubectl apply -f issuer-ephemeralCA-spiffe-istio-system.yamlCreate istio-root-ca secret in the cert-manager namespace.
This secret will contain the CA cert trust anchor used by the Istio-Envoy Proxy.
kubectl create secret generic -n cert-manager istio-root-ca --from-file=<ManagementCA-File>=ca.pemNext, create a value file in YAML format that will be used to deploy the Cert-Manager Istio CSR Plugin for the primary cluster.
cat > istio-csr-override-cluster1.yaml <<EOF
replicaCount: 1
image:
repository: quay.io/jetstack/cert-manager-istio-csr
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
imagePullSecrets: []
service:
type: ClusterIP
port: 443
app:
logLevel: 1 # 1-5
metrics:
port: 9402
service:
enabled: true
type: ClusterIP
servicemonitor:
enabled: false
prometheusInstance: default
interval: 10s
scrapeTimeout: 5s
labels: {}
readinessProbe:
port: 6060
path: "/readyz"
certmanager:
namespace: istio-system
preserveCertificateRequests: false
additionalAnnotations: []
issuer:
name: istio-system-spiffe
kind: Issuer
group: ejbca-issuer.keyfactor.com
tls:
trustDomain: "cluster.local"
rootCAFile: /var/run/secrets/istio-csr/ca.pem
certificateDNSNames:
- cert-manager-istio-csr.cert-manager.svc
certificateDuration: 24h
istiodAdditionalDNSNames: []
istiodCertificateDuration: 24h
istiodCertificateRenewBefore: 30m
istiodCertificateEnable: true
istiodPrivateKeySize: 2048
server:
clusterID: "cluster1"
#clusterID: "cluster2"
maxCertificateDuration: 48h
serving:
address: 0.0.0.0
port: 6443
certificateKeySize: 2048
signatureAlgorithm: "RSA"
#signatureAlgorithm: "ECDSA"
istio:
revisions: ["default"]
namespace: istio-system
controller:
leaderElectionNamespace: istio-system
volumes:
volumes:
- name: root-ca
secret:
secretName: istio-root-ca
volumeMounts:
- name: root-ca
mountPath: /var/run/secrets/istio-csr
resources: {}
affinity: {}
tolerations: []
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
commonLabels: {}
EOFInstall cert-manager-istio-csr Helm chart.
helm install -n cert-manager cert-manager-istio-csr jetstack/cert-manager-istio-csr -f istio-csr-override-cluster1.yamlInstall Istio components
In this section, you will install the Istio components required by the Istio Primary Cluster Control Plane: Istio Base, Istio-CNI, and the Istio Control Plane. The Primary Cluster Control Plane will contain all the Envoy proxy mTLS enrollment settings that are pushed to gateways and Envoy sidecars.
Install Istio Base via Helm:
helm install istio-base istio/base -n istio-system Install Istio-CNI:
helm install istio-cni istio/cni -n kube-system --wait\
--set "cni.cniBinDir=/var/snap/microk8s/current/opt/cni/bin" \
--set "cni.cniConfDir=/var/snap/microk8s/current/args/cni-network"Create an istio-override-mc values YAML file. This file contains all the settings that will be used to configure the Istio-Control Plane.
cat > istio-override-mc.yaml <<EOF
defaults:
## Discovery Settings
pilot:
autoscaleEnabled: true
autoscaleMin: 1
autoscaleMax: 5
autoscaleBehavior: {}
replicaCount: 1
rollingMaxSurge: 100%
rollingMaxUnavailable: 25%
hub: ""
tag: ""
variant: ""
image: pilot
traceSampling: 1.0
# Resources for a small pilot install
resources:
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 2048Mi
seccompProfile: {}
cni:
repair:
enabled: true
enabled: true
provider: default
extraContainerArgs:
- --tlsCertFile=/etc/cert-manager/tls/tls.crt
- --tlsKeyFile=/etc/cert-manager/tls/tls.key
- --caCertFile=/etc/cert-manager/ca/root-cert.pem
env:
ENABLE_CA_SERVER: false
taint:
enabled: false
namespace: ""
affinity: {}
tolerations: []
cpu:
targetAverageUtilization: 80
memory: {}
# Additional volumeMounts to the istiod container
volumeMounts:
- name: cert-manager
mountPath: /etc/cert-manager/tls
readOnly: true
- name: istio-csr-ca-configmap
mountPath: /etc/cert-manager/ca
readOnly: true
# Additional volumes to the istiod pod
volumes:
- name: cert-manager
secret:
defaultMode: 420
secretName: istiod-tls
- name: ca-root-cert
configMap:
name: istio-ca-root-cert
optional: true
defaultMode: 420
nodeSelector: {}
podAnnotations: {}
serviceAnnotations: {}
serviceAccountAnnotations: {}
topologySpreadConstraints: []
jwksResolverExtraRootCA: ""
configSource:
subscribedResources: []
keepaliveMaxServerConnectionAge: 30m
deploymentLabels: {}
configMap: true
podLabels: {}
ipFamilyPolicy: ""
ipFamilies: []
sidecarInjectorWebhook:
neverInjectSelector: []
alwaysInjectSelector: []
injectedAnnotations: {}
enableNamespacesByDefault: false
reinvocationPolicy: Never
rewriteAppHTTPProbe: true
templates: {}
defaultTemplates: []
istiodRemote:
injectionURL: ""
injectionPath: "/inject"
injectionCABundle: ""
telemetry:
enabled: true
v2:
enabled: true
prometheus:
enabled: true
stackdriver:
enabled: false
revision: ""
revisionTags: []
ownerName: ""
meshConfig:
enableTracing: true
defaultConfig:
trustDomain: cluster.local
tracing:
sampling: 50
enableTracing: true
enablePrometheusMerge: true
experimental:
stableValidationPolicy: false
global:
istioNamespace: istio-system
certSigners:
- issuers.ejbca-issuer.keyfactor.com/istio-system-spiffe
defaultPodDisruptionBudget:
enabled: true
defaultResources:
requests:
cpu: 10m
# memory: 128Mi
# limits:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 128Mi
hub: docker.io/istio
tag: 1.22.2
variant: ""
imagePullPolicy: ""
imagePullSecrets: []
istiod:
enableAnalysis: false
logAsJson: false
logging:
level: "default:info"
omitSidecarInjectorConfigMap: false
operatorManageWebhooks: false
priorityClassName: ""
proxy:
image: proxyv2
autoInject: enabled
clusterDomain: "cluster.local"
componentLogLevel: "misc:error"
enableCoreDump: false
excludeInboundPorts: ""
includeInboundPorts: "*"
includeIPRanges: "*"
excludeIPRanges: ""
includeOutboundPorts: ""
excludeOutboundPorts: ""
# Log level for proxy, applies to gateways and sidecars.
# Expected values are: trace|debug|info|warning|error|critical|off
logLevel: warning
privileged: false
readinessFailureThreshold: 4
readinessInitialDelaySeconds: 0
readinessPeriodSeconds: 15
startupProbe:
enabled: true
failureThreshold: 600 # 10 minutes
# Resources for the sidecar.
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 2000m
memory: 1024Mi
statusPort: 15020
tracer: "none"
proxy_init:
image: proxyv2
remotePilotAddress: ""
caAddress: "cert-manager-istio-csr.cert-manager.svc:443"
externalIstiod: false
configCluster: false
configValidation: true
meshID: "mesh1"
meshNetworks: {}
# Use the user-specified, secret volume mounted key and certs for Pilot and workloads.
mountMtlsCerts: false
multiCluster:
enabled: true
clusterName: "cluster1"
network: "network1"
pilotCertProvider: istiod
sds:
token:
aud: istio-ca
sts:
servicePort: 0
# The name of the CA for workload certificates.
# For example, when caName=GkeWorkloadCertificate, GKE workload certificates
# will be used as the certificates for workloads.
# The default value is "" and when caName="", the CA will be configured by other
# mechanisms (e.g., environmental variable CA_PROVIDER).
caName: ""
autoscalingv2API: true
base:
enableIstioConfigCRDs: true
istio_cni:
chained: true
provider: default
EOFInstall Istiod:
helm -n istio-system install istiod istio/istiod --wait -f istio-override-mc.yamlInstall Istio Gateway
To install the Istio Gateway used for Primary/Remote cluster communication:
Create istio-ingress values override yaml file for the istio gateway:
cat > gateway-override-mc.yaml <<EOF
# "defaults" is a workaround for Helm limitations. Users should NOT set ".defaults" explicitly, but rather directly set the fields internally.
# For instance, instead of `--set defaults.foo=bar`, just set `--set foo=bar`.
defaults:
# Name allows overriding the release name. Generally this should not be set
name: "istio-gateway-mc"
# revision declares which revision this gateway is a part of
revision: ""
# Controls the spec.replicas setting for the Gateway deployment if set.
# Otherwise defaults to Kubernetes Deployment default (1).
replicaCount:
kind: Deployment
rbac:
# If enabled, roles will be created to enable accessing certificates from Gateways. This is not needed
# when using http://gateway-api.org/.
enabled: true
serviceAccount:
# If set, a service account will be created. Otherwise, the default is used
create: true
# Annotations to add to the service account
annotations: {}
# The name of the service account to use.
# If not set, the release name is used
name: ""
podAnnotations:
prometheus.io/port: "15020"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
prometheus.io/path: "/stats/prometheus"
inject.istio.io/templates: "gateway"
sidecar.istio.io/inject: "true"
# Define the security context for the pod.
# If unset, this will be automatically set to the minimum privileges required to bind to port 80 and 443.
# On Kubernetes 1.22+, this only requires the `net.ipv4.ip_unprivileged_port_start` sysctl.
securityContext: {}
containerSecurityContext: {}
service:
# Type of service. Set to "None" to disable the service entirely
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- name: status-port
port: 15021
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 15021
- name: http2
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 443
annotations: {}
loadBalancerIP: ""
loadBalancerSourceRanges: []
externalTrafficPolicy: ""
externalIPs: []
ipFamilyPolicy: ""
ipFamilies: []
## Whether to automatically allocate NodePorts (only for LoadBalancers).
# allocateLoadBalancerNodePorts: false
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 2000m
memory: 1024Mi
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 5
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 80
targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage: {}
autoscaleBehavior: {}
# Pod environment variables
env:
# Labels to apply to all resources
labels:
operator.istio.io/component: IngressGateways
version: '1.22.2'
# Annotations to apply to all resources
annotations: {}
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
topologySpreadConstraints: []
affinity: {}
# If specified, the gateway will act as a network gateway for the given network.
networkGateway: "network1"
# Specify image pull policy if default behavior isn't desired.
# Default behavior: latest images will be Always else IfNotPresent
imagePullPolicy: ""
imagePullSecrets: []
# This value is used to configure a Kubernetes PodDisruptionBudget for the gateway.
#
# By default, the `podDisruptionBudget` is disabled (set to `{}`),
# which means that no PodDisruptionBudget resource will be created.
#
# To enable the PodDisruptionBudget, configure it by specifying the
# `minAvailable` or `maxUnavailable`. For example, to set the
# minimum number of available replicas to 1, you can update this value as follows:
#
# podDisruptionBudget:
# minAvailable: 1
#
# Or, to allow a maximum of 1 unavailable replica, you can set:
#
# podDisruptionBudget:
# maxUnavailable: 1
#
# You can also specify the `unhealthyPodEvictionPolicy` field, and the valid values are `IfHealthyBudget` and `AlwaysAllow`.
# For example, to set the `unhealthyPodEvictionPolicy` to `AlwaysAllow`, you can update this value as follows:
#
# podDisruptionBudget:
# minAvailable: 1
# unhealthyPodEvictionPolicy: AlwaysAllow
#
# To disable the PodDisruptionBudget, you can leave it as an empty object `{}`:
#
# podDisruptionBudget: {}
#
podDisruptionBudget: {}
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
# A list of `Volumes` added into the Gateway Pods. See
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes/.
volumes: []
# A list of `VolumeMounts` added into the Gateway Pods. See
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes/.
volumeMounts: []
# Configure this to a higher priority class in order to make sure your Istio gateway pods
# will not be killed because of low priority class.
# Refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/pod-priority-preemption/#priorityclass
# for more detail.
priorityClassName: ""
EOFDeploy istio gateway to the istio-ingress namespace:
helm install istio-ingress istio/gateway -n istio-system -f gateway-override-mc.yaml --waitCreate a YAML file that will be used to create a gateway and virtual service resources. These resources will provide an ingress to the Primary cluster from the Remote Cluster.
cat > istio-gw-vs.yaml <<EOF
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: istiod-gateway
spec:
selector:
# the value selector needs to match the istio= lable
istio: gateway-mc
servers:
- port:
name: tls-istiod
number: 15012
protocol: tls
tls:
mode: PASSTHROUGH
hosts:
- "*"
- port:
name: tls-istiodwebhook
number: 15017
protocol: tls
tls:
mode: PASSTHROUGH
hosts:
- "*"
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: istiod-vs
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- istiod-gateway
tls:
- match:
- port: 15012
sniHosts:
- "*"
route:
- destination:
host: istiod.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 15012
- match:
- port: 15017
sniHosts:
- "*"
route:
- destination:
host: istiod.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 443
EOFApply the
istio-gw-vs.yamlfile to the primary cluster to enable inbound access to Istio
kubectl apply -f istio-gw-vs.yamlYou have now completed the configuration of the Istio Primary Cluster and all dependencies. Istio is configured to use EJBCA for all certificates used by the Gateways and Envoy side cars.
Step 3 - Deploy Remote Cluster
This step guides you through the process of configuring the Remote MicroK8s VM as the Istio Remote instance. As part of this procedure, you will install Cert-Manager, Cert-Manager Istio-CSR, Keyfactor EJBCA Cert-Manager Issuer. Components of Istio will also be installed on the remote cluster however no Control Plane is needed on the Remote Cluster since the Primary cluster will server as the Remote Cluster’s control plane.
Add required repositories
First, add all the required repos to the Remote Cluster MicroK8s VM.:
To add the Helm repos.
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm repo add istio https://istio-release.storage.googleapis.com/charts
helm repo add ejbca-issuer https://keyfactor.github.io/ejbca-cert-manager-issuer
helm repo update
Deploy cert-manager tools
This section covers how to Install Cert-Manager, Keyfactor EJBCA Cert-Manager Issuer, and the Cert-Manager Istio CSR Plugin for Cert-Manager on the Remote Cluster.
Install Cert-Manager via Helm:
helm install \
cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \
--namespace cert-manager \
--create-namespace \
--set crds.enabled=trueInstall EJBCA Cert-Manager custom issuer
helm install ejbca-cert-manager-issuer ejbca-issuer/ejbca-cert-manager-issuer \
--namespace ejbca-issuer-system \
--create-namespaceCreate ejbca-secret by using ejbca-issuer certificate and key files that was created in Step 1 - EJBCA Preparation.
kubectl -n ejbca-issuer-system create secret tls ejbca-client-secret --cert=ejbca-issuer.pem --key=ejbca-issuer.keyCreate an ejbca-ca-secret using the Management CA certificate that was created Step 1 - EJBCA Preparation.
kubectl -n ejbca-issuer-system create secret generic ejbca-ca-secret --from-file=<ManagementCA-File>.pemCreate istio-system namespace:
kubectl create ns istio-systemCreate the istio-root-ca secret in the cert-manager namespace:
kubectl create secret generic -n cert-manager istio-root-ca --from-file=<ManagementCA-File>.pem=ca.pemCreate ejbca-cert-manager-issuer and apply it to the cluster:
cat > issuer-ephemeralCA-spiffe-istio-system.yaml <<EOF
apiVersion: ejbca-issuer.keyfactor.com/v1alpha1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
namespace: istio-system
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: issuer
app.kubernetes.io/instance: istio-system-spiffe
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ejbca-issuer
app.kubernetes.io/created-by: ejbca-issuer
name: istio-system-spiffe
spec:
hostname: "<insert-ejbca-fqdn-here>"
ejbcaSecretName: "ejbca-client-secret"
certificateAuthorityName: "<insert-management-ca-name-here>"
certificateProfileName: "<insert-mtls-certificate-profile-name-here>"
endEntityProfileName: "<insert-mtls-certificate-profile-name-here>"
caBundleSecretName: ejbca-ca-secret
EOF
kubectl apply -f issuer-ephemeralCA-spiffe-istio-system.yamlCreate the primary istio-csr overide values file that will be used when installing the cert-manager-istio-csr helm chart:
cat > istio-csr-override-remote.yaml <<EOF
replicaCount: 1
image:
repository: quay.io/jetstack/cert-manager-istio-csr
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
imagePullSecrets: []
service:
type: ClusterIP
port: 443
app:
logLevel: 1 # 1-5
metrics:
port: 9402
service:
enabled: true
type: ClusterIP
servicemonitor:
enabled: false
prometheusInstance: default
interval: 10s
scrapeTimeout: 5s
labels: {}
readinessProbe:
port: 6060
path: "/readyz"
certmanager:
namespace: istio-system
preserveCertificateRequests: false
additionalAnnotations: []
issuer:
name: istio-system-spiffe
kind: Issuer
group: ejbca-issuer.keyfactor.com
tls:
trustDomain: "cluster.local"
rootCAFile: /var/run/secrets/istio-csr/ca.pem
certificateDNSNames:
- cert-manager-istio-csr.cert-manager.svc
certificateDuration: 24h
istiodAdditionalDNSNames: []
istiodCertificateDuration: 24h
istiodCertificateRenewBefore: 30m
istiodCertificateEnable: true
istiodPrivateKeySize: 2048
server:
#clusterID: "cluster1"
clusterID: "cluster2"
maxCertificateDuration: 48h
serving:
address: 0.0.0.0
port: 6443
certificateKeySize: 2048
signatureAlgorithm: "RSA"
#signatureAlgorithm: "ECDSA"
istio:
revisions: ["default"]
namespace: istio-system
controller:
leaderElectionNamespace: istio-system
volumes:
- name: root-ca
secret:
secretName: istio-root-ca
volumeMounts:
- name: root-ca
mountPath: /var/run/secrets/istio-csr
resources: {}
affinity: {}
tolerations: []
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
commonLabels: {}
EOFInstall cert-manager-istio-csr helm chart:
helm install -n cert-manager cert-manager-istio-csr jetstack/cert-manager-istio-csr -f istio-csr-override-remote.yamlInstall Istio components
In this section you will install all the istio components required for the remote cluster: Istio Base, Istio-CNI, and Istio-Remote
Install Istio-CNI from Helm:
helm install istio-cni istio/cni -n kube-system --wait\
--set "cni.cniBinDir=/var/snap/microk8s/current/opt/cni/bin" \
--set "cni.cniConfDir=/var/snap/microk8s/current/args/cni-network"Annotate istio-system namespace. This lets Istio know that cluster1 is the control plane.
kubectl annotate namespace istio-system topology.istio.io/controlPlaneClusters=cluster1Create an istiod remote override values file. The remote override values file configures the Istio Remote cluster with the settings to connect to primary cluster1 control plane so Envoy side cars and Gateway Pods mTLS settings can be pushed from the Primary Cluster1 to the Remote Cluster2.
cat > istio-remote-override-mc.yaml <<EOF
defaults:
pilot:
autoscaleEnabled: true
autoscaleMin: 1
autoscaleMax: 5
autoscaleBehavior: {}
replicaCount: 1
rollingMaxSurge: 100%
rollingMaxUnavailable: 25%
hub: ""
tag: ""
variant: ""
image: pilot
traceSampling: 1.0
resources:
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 2048Mi
seccompProfile: {}
cni:
enabled: false
provider: default
extraContainerArgs: []
env: {}
taint:
enabled: false
namespace: ""
affinity: {}
tolerations: []
cpu:
targetAverageUtilization: 80
memory: {}
volumeMounts: []
volumes: []
nodeSelector: {}
podAnnotations: {}
serviceAnnotations: {}
serviceAccountAnnotations: {}
topologySpreadConstraints: []
jwksResolverExtraRootCA: ""
configSource:
subscribedResources: []
keepaliveMaxServerConnectionAge: 30m
deploymentLabels: {}
configMap: true
podLabels: {}
ipFamilyPolicy: ""
ipFamilies: []
trustedZtunnelNamespace: ""
sidecarInjectorWebhook:
neverInjectSelector: []
alwaysInjectSelector: []
injectedAnnotations: {}
enableNamespacesByDefault: false
reinvocationPolicy: Never
rewriteAppHTTPProbe: true
templates: {}
defaultTemplates: []
istiodRemote:
injectionURL: ""
injectionPath: "/inject/cluster/cluster2/net/network1"
injectionCABundle: "LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUZhekNDQTFPZ0F3SUJBZ0lVSUdLM3ROS3JlQXpwQ0drWW9UaUhCSXBlS1hrd0RRWUpLb1pJaHZjTkFRRU4KQlFBd1BURWVNQndHQTFVRUF3d1ZRMjl0YlhWdWFYUjVUV0Z1WVdkbGJXVnVkRU5CTVE0d0RBWURWUVFLREFWRgpTa0pEUVRFTE1Ba0dBMVVFQmhNQ1ZWTXdIaGNOTWpRd05qSTFNVFF3TmpNeldoY05NelF3TmpJek1UUXdOak15CldqQTlNUjR3SEFZRFZRUUREQlZEYjIxdGRXNXBkSGxOWVc1aFoyVnRaVzUwUTBFeERqQU1CZ05WQkFvTUJVVksKUWtOQk1Rc3dDUVlEVlFRR0V3SlZVekNDQWlJd0RRWUpLb1pJaHZjTkFRRUJCUUFEZ2dJUEFEQ0NBZ29DZ2dJQgpBSXkwQnRYbVVnTDQ5dGxIbzA5TnNweHpFRi8vSTlmZUp4bjI2a0dzaS9KaFZmQ1IzUE1MalRWb1RCbStiaFo2ClJtZlVISVdxZGlxUlNiUkVlWXdGOFMzT1krcWYxb21JYWNqeml1ZzhYcmY4WWpwZmhkRURWV0orMDB0U0RZQ3UKMG01Z244UktZL09Od0ZsVGFYVkhXcytaSWRubWdPZmhLTExDeHoxQ3QrcUNadGQrTjkvSjFtUVN5Y25xOTNvVApFU0FMRVBCMXF6QUpCdTZ2WnZNa1VGeEE2Tkc1UEtPMm04ejVYRWpWbHRDVkRLSE0rWVp2cXpQWXVMeHlocFcvCjdMUG43aHpVZ2JVazI1dk5zVmlMNmNVVm56Z1NnYWpXR0phSHltTTRrc1NvQ3VPQk1udjFha1BnU0oxWlY3Q0kKd2diUzJqcEw5TmxCM2lCK0hSMjJDell6MmVub2ZIRW9zdUZFZVc3NW8xdXpkODJlenBSeVZQc3c3NG9kNVZrVgo1UUlDR3JjYUFWT09XRXhTN1A5cXBRc1pyMkJaU0dQeDVpK3N0dU1VTEFnVSt5Qk1zN1JGK2Jra2Q0NmZRdFR1CjdkeFpCWXpHMTlIRjhlYjhrbXdNNWtYNXJEOEMvRllqbG9vZlJVVk8rMFdVTkJVQkVqMmVDRXkwT3ltd0lZeW4KRm5WZTdvZUVYL0kxbkJySkdOdHFkUWRZcnpzcTlhenMwZHBJYlZReEVQT05ybjhjdDdpdjlhTURuR0NGeFZ5cwpaby9iOXpLNElFeUVhNzhocGw5M2dySW93K3oxaG9OSXN1dDlWVFFBU0ZmTzNCZm9ablZ3NWRxTHc4NGUwblVICkRVSEhsV1N3UmpndTB3M0RNczhncGVCS0crWFgxZlJMWUZYWXh6TlM1cnFWQWdNQkFBR2pZekJoTUE4R0ExVWQKRXdFQi93UUZNQU1CQWY4d0h3WURWUjBqQkJnd0ZvQVVOcEQwN2lvem9vM0UxdzJ4YlBIeW1aay9UY1F3SFFZRApWUjBPQkJZRUZEYVE5TzRxTTZLTnhOY05zV3p4OHBtWlAwM0VNQTRHQTFVZER3RUIvd1FFQXdJQmhqQU5CZ2txCmhraUc5dzBCQVEwRkFBT0NBZ0VBYjliM2RVNWdHU3VYc09OT0tCcElBNUFWZE9GYS9VeE5hVEJtbDdxTDIyaDIKcTFNZm5XZnVjTGhoak0vOHNjWEpIYnBBNDRST1NjZHZOaFRPajh1RmRTam9oZitiaDF2MEhxeG81YUlDRzhYVwpQNzdYOSs1d0RHZ3hpa01tcis3dnVncDNwOXp4Nkh4VnJXZmdmWHZpV1JQbFEzYUJjcmRBWUFzaW9OR0g0TnZDCjFrU2lVa2FPRFRFR1htNy9rV1FOWFBiSDI3Z1NqQzF2RjhSamkrZXlwcUtPU0lOamJ3U25rS0Q3WDVTeHVUK1IKbUEzWUxZT1VzemFmVm5LMytCUFZhbDhjUFk2M1N4THN4TVB3dE4wN3htc1JDTmZlMkEyc0krTVViUm9VSWhvcApodDVDOUpOa24vTUtDd01xKzJoU29ZeTl1VllXNk1hTWRXVW5ldnJGWXlXSDdVTlJOcXAra0FOTkk5dTA0aVZzClpjblRQTWJTQjhlbWdoWXl5dm5xVXNuSUNKWmJhQWF2SFk1Qy9TWHA4a0Q3aXNwNVhrRTdtYzhHUlpUVzJBVWQKcVVWLzBic0tEa3J1NkIzWGk0LzdjYUp1bzFTNktMVU4zZE1YVVdyME5oTWtRZVFzenNzYnlvRG56dWtiTncrUQpiMlcrY3dMZFdSbGc4SmR5Wmd2YTdpdXRxMm1VR0hOM0J0R1ZKMmhqNjdIUG55b1U1K29CdzVnT2FhR2NoZHp1Cjd1cmFKOE0rSE90NkZHMVNSSkoyUmUyZzVseENNWmlaa3FBZlVJVysxQ2E1dk1jMCtQUHNlVldkd2tPVzhwM24KODVXQ3dVdmtyQ1hEZGZ6cFBjbnVKMld1NFBrQUsybGN0UXdrVUN4bFJxSFkyQzBmZFZuRW1pQStteUdPWFhJPQotLS0tLUVORCBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0t"
telemetry:
enabled: false
v2:
enabled: true
prometheus:
enabled: true
stackdriver:
enabled: false
revision: ""
revisionTags: []
ownerName: ""
meshConfig:
enablePrometheusMerge: true
experimental:
stableValidationPolicy: false
global:
istioNamespace: istio-system
certSigners: []
defaultPodDisruptionBudget:
enabled: true
defaultResources:
requests:
cpu: 10m
hub: docker.io/istio
tag: 1.22.2
variant: ""
imagePullPolicy: ""
imagePullSecrets: []
istiod:
enableAnalysis: false
logAsJson: false
logging:
level: "default:info"
omitSidecarInjectorConfigMap: true
operatorManageWebhooks: false
priorityClassName: ""
proxy:
image: proxyv2
autoInject: enabled
clusterDomain: "cluster.local"
componentLogLevel: "misc:error"
enableCoreDump: false
excludeInboundPorts: ""
includeInboundPorts: "*"
includeIPRanges: "*"
excludeIPRanges: ""
includeOutboundPorts: ""
excludeOutboundPorts: ""
logLevel: warning
outlierLogPath: ""
privileged: false
readinessFailureThreshold: 4
readinessInitialDelaySeconds: 0
readinessPeriodSeconds: 15
startupProbe:
enabled: true
failureThreshold: 600
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 2000m
memory: 1024Mi
statusPort: 15020
tracer: "none"
proxy_init:
image: proxyv2
remotePilotAddress: "192.168.5.106"
caAddress: ""
externalIstiod: true
configCluster: true
configValidation: true
meshID: "mesh1"
meshNetworks: {}
mountMtlsCerts: false
multiCluster:
enabled: false
clusterName: "cluster2"
network: "network1"
pilotCertProvider: istiod
sds:
token:
aud: istio-ca
sts:
servicePort: 0
caName: ""
autoscalingv2API: true
base:
enableIstioConfigCRDs: true
istio_cni:
chained: true
provider: default
gateways:
securityContext: {}
EOFThe Istio Remote Helm chart is not hosted and must be installed by download the Istio source code from github. To do this run the following git command.
git clone https://github.com/istio/istio.gitInstall Istiod on cluster2 leveraging the istio source code manifest repository.
helm install -f remote-override-mc.yaml -n istio-system istio-remote /<path to source>/istio/manifests/charts/istiod-remote --waitIstio is now installed on the secondary cluster.
Step 4 - Create Istio credentials
In this section, you will create remote secrets (kube-configs) that will be used to authenticate to the Kubernetes API for Istio authentication. Istio will use these secrets for cluster-to-cluster authentication.
For the clusters to connect, they need to share credentials.
On the primary cluster, run the following to create the cluster1-secret.yaml file. This file will then be applied to the secondary cluster.
istioctl create-remote-secret --name=cluster1 > cluster1-secret.yamlOn the secondary cluster, run the following command:
istioctl create-remote-secret --name=cluster2 > cluster2-secret.yamlCopy cluster 1 secret to cluster 2.
Copy cluster 2 secret to cluster 1.
On Cluster 1, run the following command to apply the cluster2-secret:
kubectl apply -f cluster2-secret.yamlOn Cluster 2, run the following command to apply the cluster1-secret:
kubectl apply -f cluster1-secret.yamlYou now have completed all required steps to set up Istio in a Primary-Remote Multi-Cluster using EJBCA as the sole PKI provider for all certificates used by Istio.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned how to set up Istio in a multi-cluster Kubernetes environment using EJBCA as an external CA.
Here are some next steps we recommend:
If you are interested in EJBCA Enterprise, read more on Keyfactor EJBCA Enterprise.
If you are interested in EJBCA Community, check out EJBCA Community vs Enterprise or read more on ejbca.org.
If you are an EJBCA Enterprise customer and need support, visit the Keyfactor Support Portal.
Discuss with the EJBCA Community on GitHub Discussions.
.png)