Deploy RA and VA in Kubernetes
ENTERPRISE
For improved performance and security, EJBCA Enterprise can be set up to communicate with other instances of EJBCA acting as Registration Authority (RA) and/or Validation Authority (VA) using the peer protocol. The EJBCA Enterprise RA and VA containers are deployed using the EJBCA Enterprise Edition Helm chart, see EJBCA Container Set.
The following outlines how to customize Helm Chart parameters to deploy RA and/or VA instances and how to configure peer communication with a CA instance.
The deployment uses a LoadBalancer Service with an NGINX sidecar for TLS termination. There is only a small difference if an Ingress with TLS pass through which is highlighted in the section Deploy RA and VA in Kubernetes | Difference-with-deployments-with-Ingress-with-TLS-pass-through .
If you have access to neither LoadBalancer or Ingress with TLS pass through, then see Deploy RA and VA in Kubernetes with NGINX Ingress.
Overview
When deploying EJBCA with a LoadBalancer Service, an NGINX or Apache HTTPD sidecar is used to manage incoming traffic. Kubernetes Secrets are used to configure the sidecar with TLS credentials.
Multiple domains can be configured, each with its own TLS certificate issued by different Certificate Authorities (CAs). The sidecar uses TLS Server Name Indication (SNI) to select the appropriate certificate and trusted CA. All configured domains are accessible through the same external IP address provided by the LoadBalancer Service.
For details on Helm Chart parameters related to LoadBalancer configuration, see EJBCA Helm Deployment Parameters.
Step 1 - Set up TLS credentials
The server TLS certificate is issued and configured for use by the NGINX sidecar as a Kubernetes Secret. The certificate includes DNS names used to access the RA or VA both externally and internally.
Certificate naming considerations
Assume the external domain ejbcara.example.com is used to access the RA or VA from outside the cluster. This domain must be included:
In the Subject DN as the Common Name (CN)
In the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) as a DNS Name
Internal access domains depend on the Helm release name and Kubernetes namespace and must also be included in the SAN. For example, when the Helm release name is ejbca-ra-deploy and the namespace is ranamespace, valid internal DNS names include:
ejbca-ra-deploy-nginx.ranamespaceejbca-ra-deploy-nginx.ranamespace.svc.cluster.local
The -nginx or -httpd suffix is added based on the sidecar in use. These internal domains are used by applications within the same cluster (for example REST API or ACME clients).
For RA deployments only, multiple replicas may be deployed. In this case, an additional wildcard DNS name must be included in the SAN to allow the CA to connect to individual RA pods:
ejbca-ra-deploy-nginx-per-pod-*.ranamespaceejbca-ra-deploy-nginx-per-pod-*.ranamespace.svc.cluster.local
Only a single VA instance should be deployed per Helm installation, as each VA must connect to a separate database.
Example certificate configuration
Subject DN: CN=ejbcara.example.com
SAN:
dnsName=ejbcara.example.com
dnsName=ejbca-ra-deploy-nginx.ranamespace
dnsName=ejbca-ra-deploy-nginx-per-pod-*.ranamespaceEnroll server TLS certificate
You can follow the same procedure described in Deploy CA in Kubernetes to enroll a TLS certificate for a VA.
For RA deployments, you must first create a dedicated End Entity Profile.
Create End Entity Profile (RA only)
[REWORDED]
Perform the following steps in the EJBCA CA Admin Web:
Navigate to RA Functions > End Entity Profiles
Click Add
Specify a name, for example
PeerServerEndEntityProfileEnsure the following configuration:
Subject DN Attributes: CN (Common Name) present and modifiable.
Subject Alternative Name: Add three DNS Name fields (modifiable).
Available Certificate Profiles: SERVER.
Default Certificate Profile: SERVER.
Default CA: ManagementCA (or adjust based on your setup).
Click Save.
Enroll server certificate
In EJBCA, click RA Web to access the EJBCA RA user interface.
Select Enroll > Make New Request and specify the following:
For Certificate Type, select PeerServerEndEntityProfile.
For Certificate subtype (if prompted), select SERVER.
For CA (if prompted), select ManagementCA.
For Key-pair generation, select By the CA.
For Key algorithm, select for example, RSA-2048, or P-256.
For the Required Subject DN Attributes, specify CN, Common Name=
ejbcara.example.com.For Subject Alternative Name Attributes, click Show more optional fields and specify DNS Names
ejbcara.example.comejbca-ra-deploy-nginx.ranamespaceorejbca-ra-deploy-nginx.ranamespace.svc.cluster.local(RA only)
ejbca-ra-deploy-nginx-per-pod-*.ranamespaceorejbca-ra-deploy-nginx-per-pod-*.ranamespace.svc.cluster.local
For Provide User Credentials, enter a username and password.
Click Download PEM to download the server certificate in PEM format.
The TLS certificates are now issued from the CA. Continue to the steps below to configure these certificates to use.
Configure internal sidecar with TLS
The internal sidecar must be configured with the enrolled TLS private key, TLS certificate, and issuing CA certificate. These components are extracted from the downloaded PEM file and stored in a Kubernetes Secret.
The filenames inside the secret are prefixed with the value of nginx.host. In this example, nginx.host is ejbca-ra-internal-host. Once the secret is created, set the nginx.secretInternalNginxCert to the name of the secret, and nginx.mountInternalNginxCert to true.
You can split the PEM file manually or use the following script.
#!/bin/bash
issued_key_pair_file="$1"
host_name="$2"
private_key_begin=$(cat "$issued_key_pair_file"|grep -n 'BEGIN PRIVATE KEY'|cut -f1 -d:)
private_key_end=$(cat "$issued_key_pair_file"|grep -n 'END PRIVATE KEY'|cut -f1 -d:)
head -n $private_key_end "$issued_key_pair_file" | tail -"$((private_key_end - private_key_begin +1))" > "$host_name-Key.pem"
ee_cert_begin=$(cat "$issued_key_pair_file"|grep -m 1 -n 'BEGIN CERTIFICATE'|cut -f1 -d:)
ee_cert_end=$(cat "$issued_key_pair_file"|grep -m 1 -n 'END CERTIFICATE'|cut -f1 -d:)
head -n $ee_cert_end "$issued_key_pair_file" | tail -"$((ee_cert_end - ee_cert_begin +1))" > "$host_name-cert.pem"
lines_in_file=$(wc -l "$issued_key_pair_file"|cut -f1 -d ' ')
tail -n "$((lines_in_file - ee_cert_end))" "$issued_key_pair_file" > "$host_name-CA-temp.pem"
sed '/Bag Attributes/d' "$host_name-CA-temp.pem" | sed '/subject=/d' | sed '/issuer=/d' | sed '/friendlyName/d' > "$host_name-CA.pem"
rm "$host_name-CA-temp.pem"Example usage:
# usage
./split-pem-full-chain.sh downloaded-file.pem ejbca-domain
# example
./split-pem-full-chain.sh ejbcara.example.com.pem ejbcara.example.com
# after the run
ls -A1
split-pem-full-chain.sh
ejbcara.example.com-cert.pem
ejbcara.example.com-Key.pem
ejbcara.example.com-CA.pem
ejbcara.example.com.pem
# then create the secret in Kubernetes to configure TLS for sidecar
kubectl create secret generic internal-nginx-credential-secret-ra1 \
--from-file=ejbcara.example.com.pem=ejbcara.example.com-cert.pem \
--from-file=ejbcara.example.com-Key.pem=ejbcara.example.com-Key.pem \
--from-file=ejbcara.example.com-CA.pem=ejbcara.example.com-CA.pemAfter running the script, you will have the following files:
ejbcara.example.com-cert.pemejbcara.example.com-Key.pemejbcara.example.com-CA.pem
Create the Kubernetes Secret
After splitting the PEM file, create a Kubernetes Secret containing the TLS credentials:
kubectl create secret generic internal-nginx-credential-secret-ra1 \
--from-file=ejbcara.example.com.pem=ejbcara.example.com-cert.pem \
--from-file=ejbcara.example.com-Key.pem=ejbcara.example.com-Key.pem \
--from-file=ejbcara.example.com-CA.pem=ejbcara.example.com-CA.pemStep 2 - Configure Helm chart parameters
Configure the Helm Chart to expose the RA or VA using a LoadBalancer Service.
nginx.host: External domain name (for exampleejbcara.example.com)nginx.service.type: Set toLoadBalancer
Apache HTTPD can be used instead of NGINX by configuring the equivalent parameters under the httpd section.
Example configuration:
image:
variant: ra
#variant: va
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
imagePullSecrets:
- name: keyfactor-registry
ejbca:
license: ejbca-license-secret
configdumpImport:
enabled: true
initialize: true
configMapName: ejbca-ra-init-configmap
configMapKey: configdump.json
env:
TLS_SETUP_ENABLED: "later"
DATABASE_JDBC_URL: "jdbc:mariadb://ra-database-service:3306/ejbca?characterEncoding=utf8"
# this parameters enable EJBCA to synchronize session data among the cluster
HIGH_AVAILABILITY: true
envRaw:
- name: DATABASE_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: ejbcadbcredentials
key: database_user
- name: DATABASE_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: ejbcadbcredentials
key: database_password
nginx:
enabled: true
host: "ejbcara.example.com"
mountInternalNginxCert: true
secretInternalNginxCert: "internal-nginx-credential-secret-ra1"
service:
type: LoadBalancer
# replicaCount: 2
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 5
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 60
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"Difference with deployments with Ingress with TLS pass through
All other deployment steps are the same as for LoadBalancer deployments, but the Helm chart uses an ingress section and omits the service.type section in the sidecar configuration.
nginx:
enabled: true
host: "ejbcara.example.com"
mountInternalNginxCert: true
secretInternalNginxCert: "internal-nginx-credential-secret-ra1"
ingress:
enabled: true
# indicates TLS pass through
sslBackend: true
hosts:
- host: "ejbcara.example.com"
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
The full example looks similar to:
image:
variant: ra
#variant: va
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
imagePullSecrets:
- name: keyfactor-registry
ejbca:
license: ejbca-license-secret
configdumpImport:
enabled: true
initialize: true
configMapName: ejbca-ra-init-configmap
configMapKey: configdump.json
env:
TLS_SETUP_ENABLED: "later"
DATABASE_JDBC_URL: "jdbc:mariadb://ra-database-service:3306/ejbca?characterEncoding=utf8"
# this parameters enable EJBCA to synchronize session data among the cluster
HIGH_AVAILABILITY: true
envRaw:
- name: DATABASE_USER
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: ejbcadbcredentials
key: database_user
- name: DATABASE_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: ejbcadbcredentials
key: database_password
nginx:
enabled: true
host: "ejbcara.example.com"
mountInternalNginxCert: true
secretInternalNginxCert: "internal-nginx-credential-secret-ra1"
ingress:
enabled: true
# indicates TLS pass through
sslBackend: true
# These annotations includes Ingress control specific configuration
# to allow TLS pass through
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTPS
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
# example: for HAProxy
# haproxy.org/ssl-passthrough: "true"
hosts:
- host: "ejbcara.example.com"
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
# replicaCount: 2
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 5
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 60
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"Step 3 - Install the Peer EJBCA
This procedure only needs to be performed once, as all peer EJBCA instances share the same database.
Import Management CA
In your browser, navigate to https://<host>/ejbca/adminweb, for example
https://ejbcara.example.com/ejbca/adminweb.
Ensure to connect over HTTPS as your browser may reject the EJBCA server certificate unless the Management CA is added to your local system as a trusted CA.
When prompted for certificate authentication, click Cancel.
Select Import a CA from existing PKI and click Next.
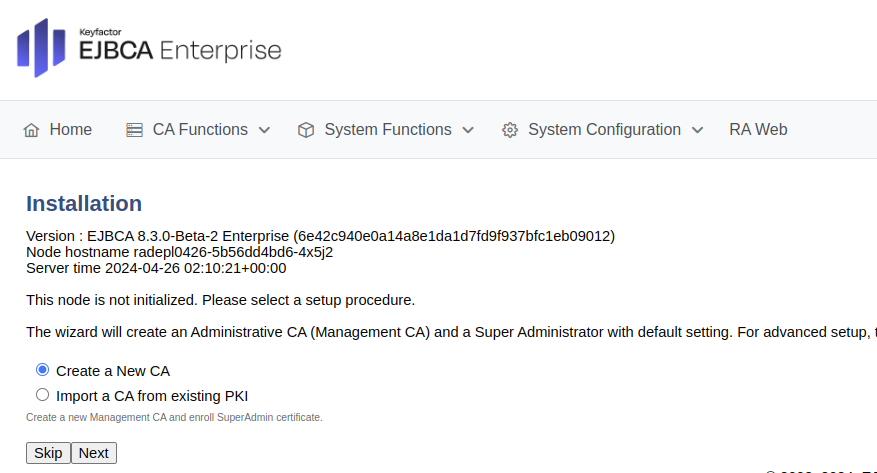
To import the Management CA certificate file downloaded from the CA instance in a previous step, do the following:
For The name this CA will be given, specify ManagementCA.
Click Browse to upload the full CA certificate ManagementCA.pem file previously downloaded.
Click Import CA certificate and click Next.
Update roles and role members
To update the Super Administrator role, perform the following steps:
Click Setup Role to go to the Roles Management page.
Next to the Super Administrator Role, click Members.
Members are defined by an attribute from the certificate DN and the serial number:
Match with: Select X509:CN, Common name.
CA: Ensure that the Management CA is selected for the CA to match on.
Match Value: Specify the CN value from the certificate, in this example: "SuperAdmin". Note that this is a case-sensitive matching.

Click Add to add the user to the Super Administrator Role.
Access EJBCA
To access EJBCA using the SuperAdmin certificate:
In your browser, navigate to the EJBCA RA instance https://<hostname>/ejbca/adminweb/ (
https://ejbcara.example.com/ejbca/adminweb).When prompted for the SuperAdmin certificate, select the correct certificate, and click OK.
To remove public access and restrict access to EJBCA to only the Super Administrator, click Remove next to “Public access with Super Administrator Role exists”.
EJBCA is now successfully deployed.
Prepare for peer connection
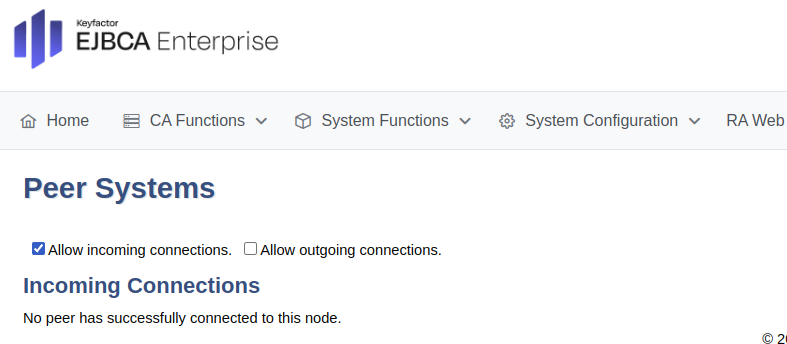
To set up the RA to allow for incoming connections, do the following:
In the EJBCA RA instance, click System Functions>Peer Systems.
Select Allow incoming connections to allow the CA to connect.
Step 4 - Configure peering in CA
Perform the following steps in the EJBCA CA Admin Web to configure peer communication.
Create Crypto Token
The following covers how to create a soft crypto token and keys. If you will use an existing token, you can skip this step.
In your browser, navigate to the EJBCA CA instance.
In the EJBCA CA instance, click System Functions>Crypto Tokens.
Click Create new and specify the following on the New Crypto Token page:
For Create Management CA, select Create New Crypto Token.
On the New Crypto Token page, specify the following:
Name: Specify a name for the crypto token, such as PeerToken.
Type: Select SOFT.
Auto-activation: Select Use to allow EJBCA to save the password and reapply it after a restart so that the CA is always available.
Authentication Code: Enter a password to be used to activate the crypto token.
Repeat Authentication Code: Re-enter the password.
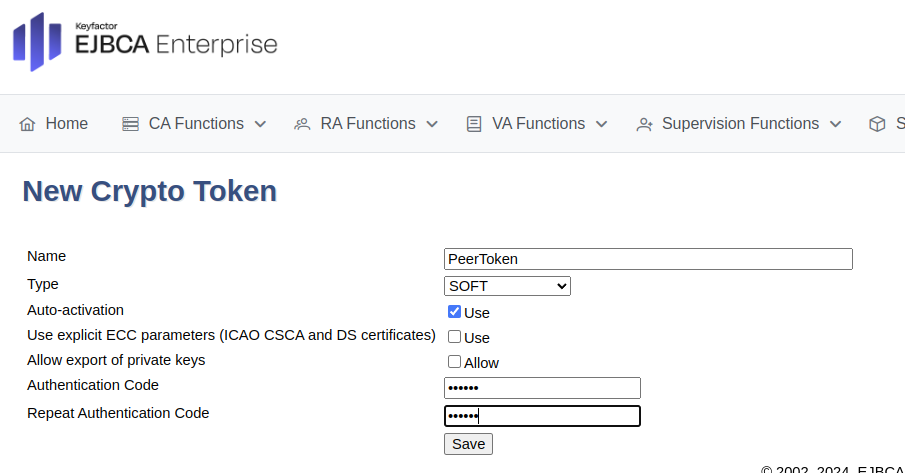
Click Save to create the crypto token.
On the Crypto Tokens page, click the created crypto token.
For the signKey, select RSA 2048, and then click Generate new key pair to create the keys.
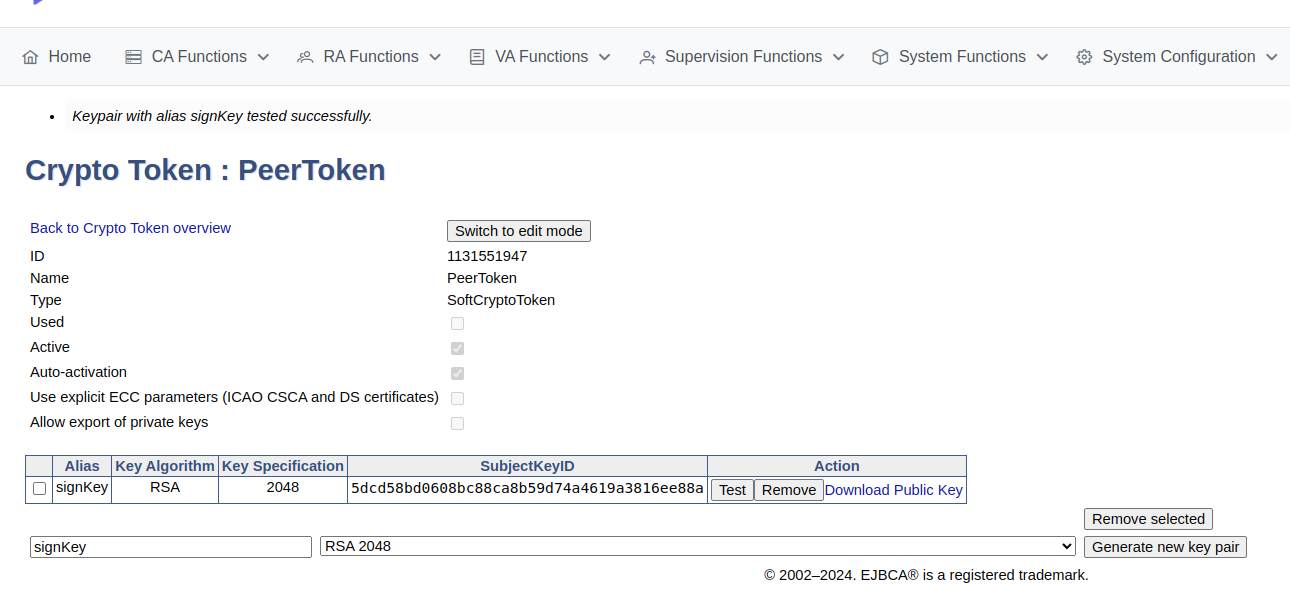
A new signKey key pair is generated and displayed in the list of key pairs
It is recommended to use RSA2048 for peer connections to ensure performance and avoid issues which may arise if using ECC keys when an HSM (P11NG) token is used.
The Administrator also needs to select the following permissions for HSM (P11NG) tokens: Sign and Encrypt.
Create Remote Authentication
To set up an remote authenticator to identify the CA to the RA:
In EJBCA, go to System Functions>Remote Authentication.
Click Create new and select the crypto token and key.
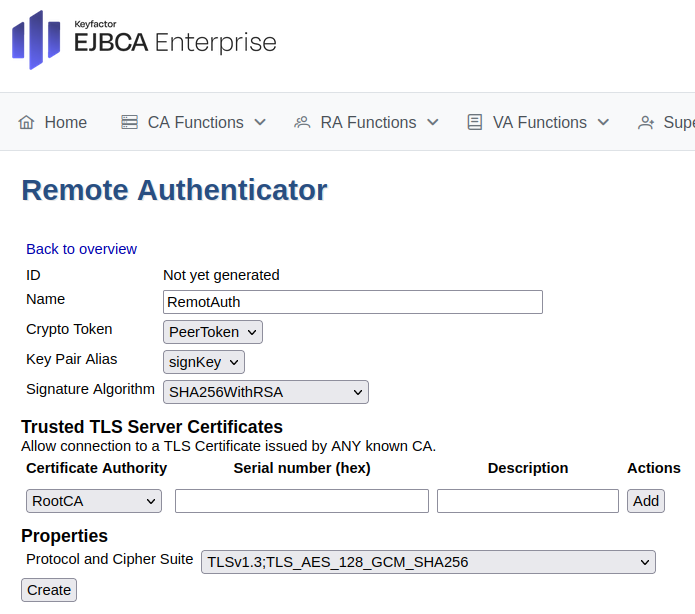
Click Create.
Back on the Remote Authentication page, click the CSR action to download the certificate signing request for the key pair.
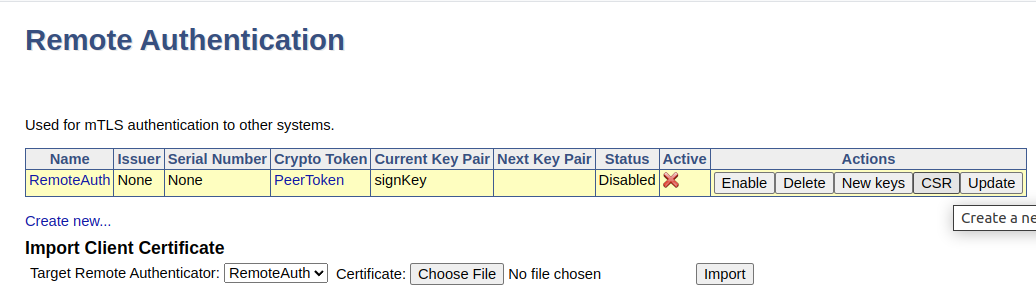
Enroll Remote Authentication
Next, to enroll the remote authentication:
In EJBCA, click RA Web to access the EJBCA RA interface.
Select Enroll > Make New Request and specify the following:
For Certificate subtype, select ENDUSER.
For Key-pair generation, select Provided by user.
Upload the CSR.
For Provide User Credentials, enter a username and password.
Click Download PEM to download the certificate in PEM format.
Go back to the Remote Authentication page, click the action Update, and then click Enable.
The remote authentication is indicated as Active in the overview.
Create Peer Connection
For a VA peer connection, leave Process incoming requests disabled. The URL format is:
https://ejbca-va-nginx.ejbca-scenario02-va/ejbca/peer/v1Unlike RA peers, there is no need to configure a separate service for each pod.
To create a peer connection, do the following:
In EJBCA, go to System Functions>Peer Systems.
Update the following:
Create peer connection for each replica for RA. The URL will be in a form
https://ejbca-ra-nginx-per-pod-*.ejbca-scenario02-ra/ejbca/peer/v1where the*is from 0 to your maximum number of replica minus 1. Hence if you set:replicaCount: 4then we need to create 4 peer connections with 0 to 3 in place of*autoscaling.maxReplicas: 5then we need to create 5 peer connections with 0 to 4 in place of*
For URL (endpoint), enter the URL for the RA instance. Depending on your setup, this is either the service corresponding to the NGINX sidecar, or the Ingress. Note that the DNS Name entered during certificate enrollment while TLS was setup, must match.
For Incoming requests, select Process incoming requests if the peer is an RA. If creating a peer connection for an VA, clear the Process incoming requests option.
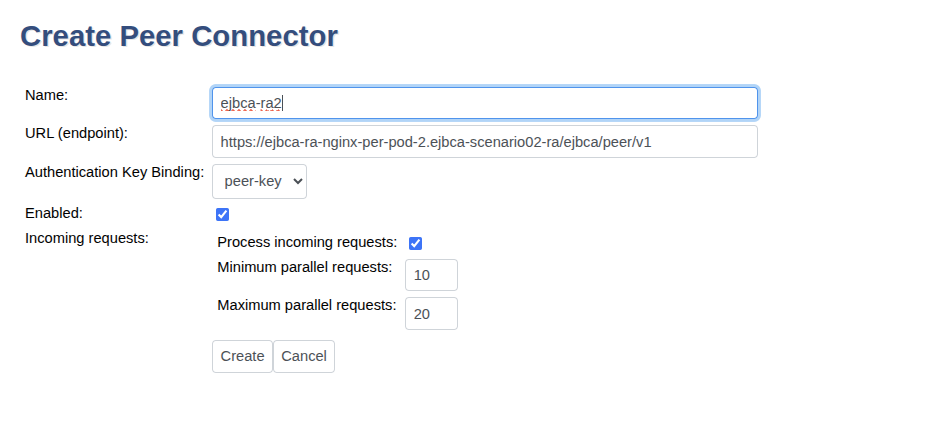
Click Create.
Click Ping to ping the remote peer. A warning with status code 401 is shown since the Peer URL is reachable but the peer does not allow access to the remote authentication key.
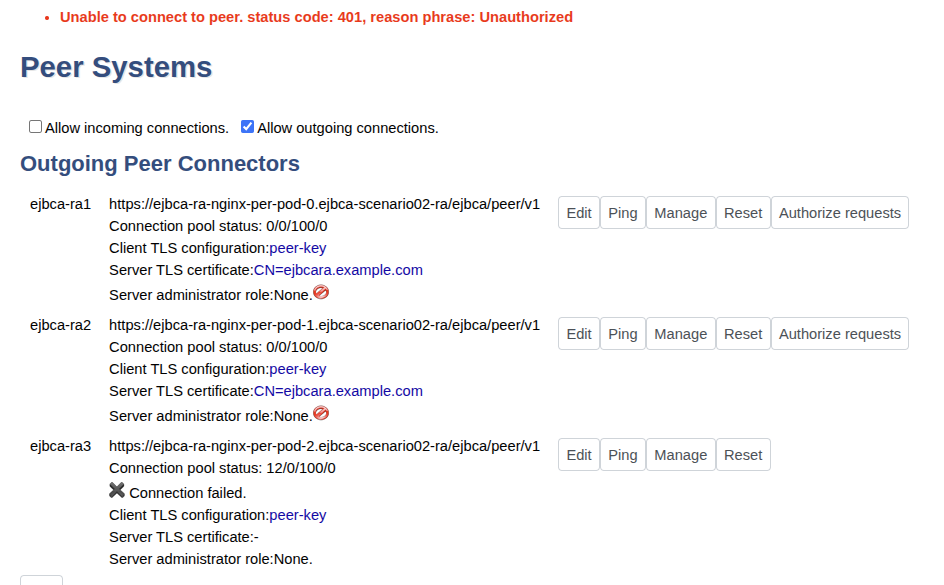
Note that the Authorize request is only visible when configuring a peer connection to an RA.
A Connection failed message appears when the RA replica is not yet deployed (for example, during auto-scaling). Once the replica is deployed, the CA automatically connects to it.
If a 401 – Unauthorized message does not appear:
Verify that the DNS Name in the server TLS certificate includes:
CODE<helm-ra-release-name>-nginx.<ra-deployment-namespace>You may also need to include the
.svc.cluster.localsuffix during certificate enrollment.If the URL is unreachable, ensure the URL format matches the example above. Confirm that the NGINX sidecar service is running, and that the namespace and release names were correctly specified during peer configuration.
If the NGINX sidecar pod is not ready, check the pod logs for errors. Misconfigured TLS secrets may also prevent successful connection.
Step 5 - Configure access rules in cluster
Next, access the RA peer instance to configure the access rules.
Authorize the remote connection in RA or VA
To set up the incoming peer connection, do the following:
Navigate to the EJBCA peer instance (for example,
https://ejbcara.example.com/ejbca/adminweb).In EJBCA, click System Functions>Peer Systems.
The incoming connection from the CA should appear in the Incoming Connections section. The CA can connect, but the RA has been given no rights.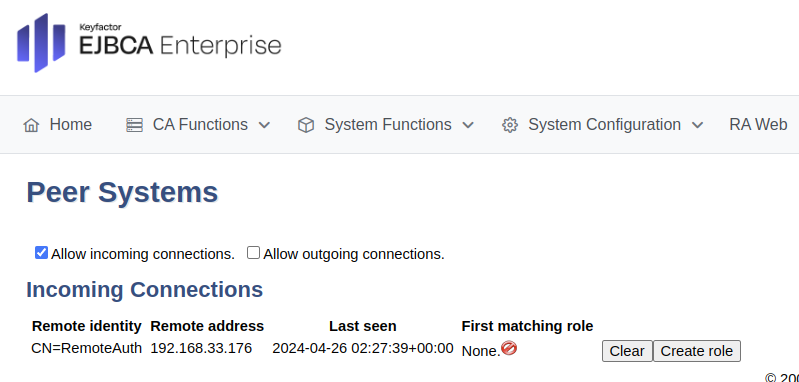
Click Create Role.
For the RA, ensure similar options are entered and then click Create new role at the bottom.

For an RA, update the following:
For Generic rules, select Role is intended for peer connections and Accept long hanging connections and ensure that Accept RA Requests is cleared.
For CAs, select Access ManagementCA.
For a VA, update the following:
Clear Accept long hanging connection.
Select all settings in the Publishing section.
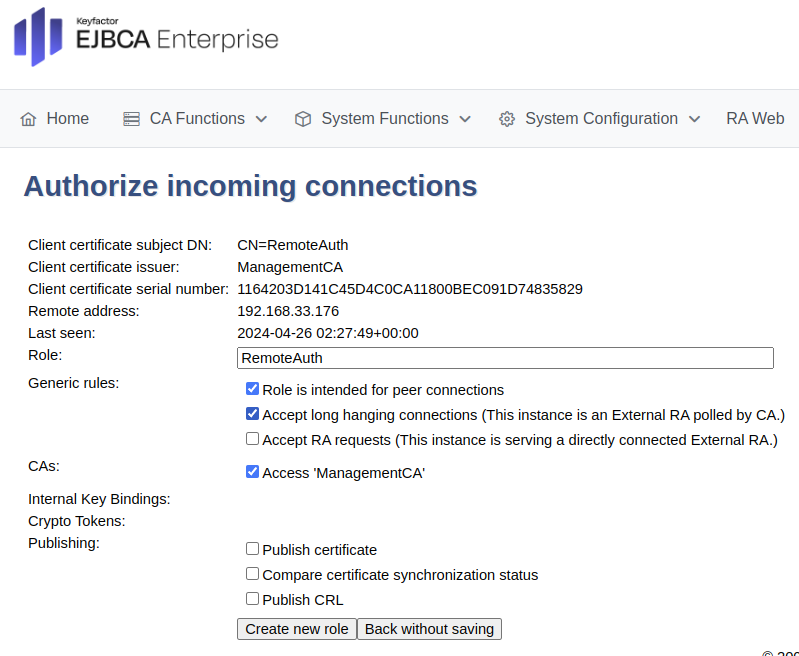
Click Create new role.
Step 6 - Configure access rules (RA only)
This step applies only to RA peers and can be skipped for VA deployments.
Configure access rules on the EJBCA CA instance following the steps below.
On the EJBCA CA instance, click System Functions>Peer Systems.
Click Peer Systems.
Click Authorize Requests.
In next page in the Role list, select Create New Role and click Select.
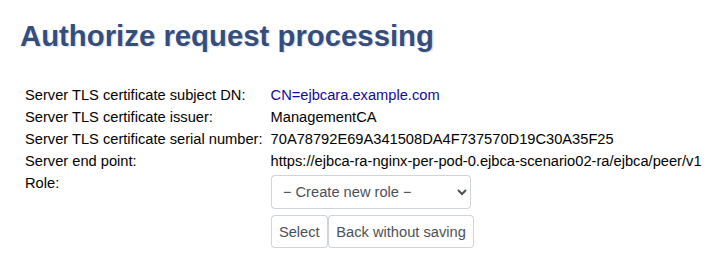
Set the following, and then click Modify role.
Select all options for all RA rules.
Select all options for Process requests for CA(s).
Select all options for Process requests for End Entity Profile(s), except EMPTY that should be cleared.
Select all options for Process requests from protocols.
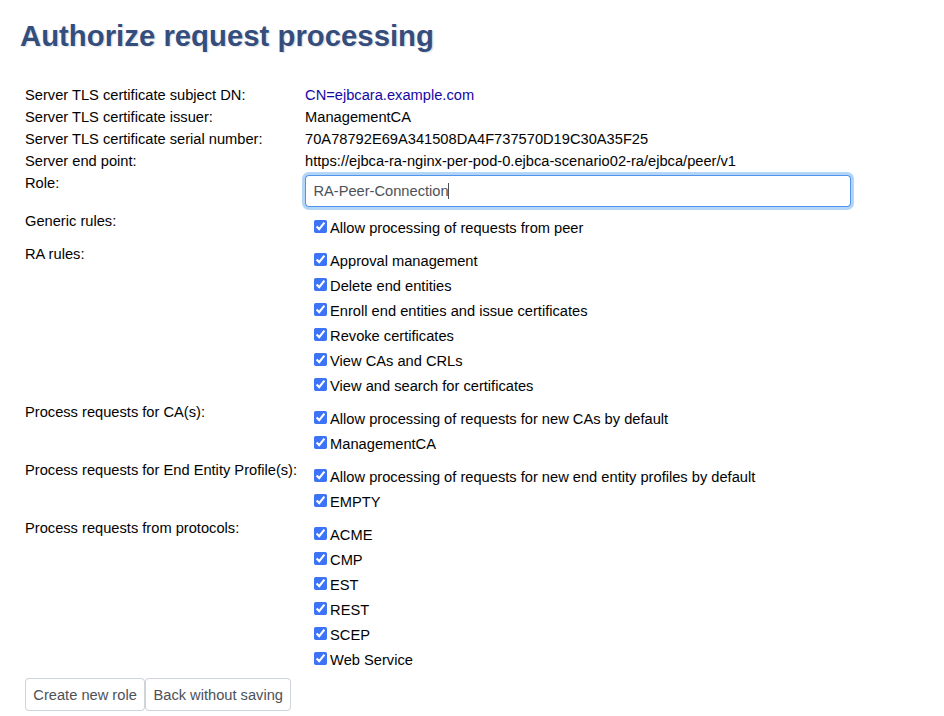
The Peer Systems page now displays the outgoing peer connectors with details for the Server administrator role for the corresponding peer. We just need to configure this for one replica.
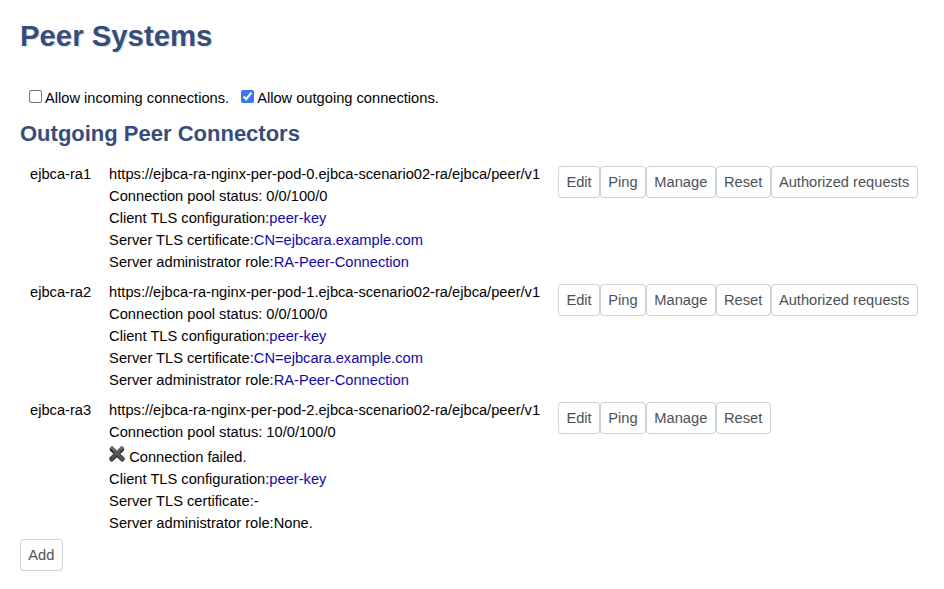
Step 7 - Verify the setup
Verify that the RA and VA instances are functioning correctly.
Verify RA
All RA instances, including those deployed during scale-up operations, are configured.
In your browser, navigate to the EJBCA RA instance https://<hostname>/ejbca/adminweb/ (
https://ejbcara.example.com/ejbca/adminweb)In EJBCA, click RA Web to access the EJBCA RA interface.
Optionally, click Search>Certificates to view enrolled certificates.
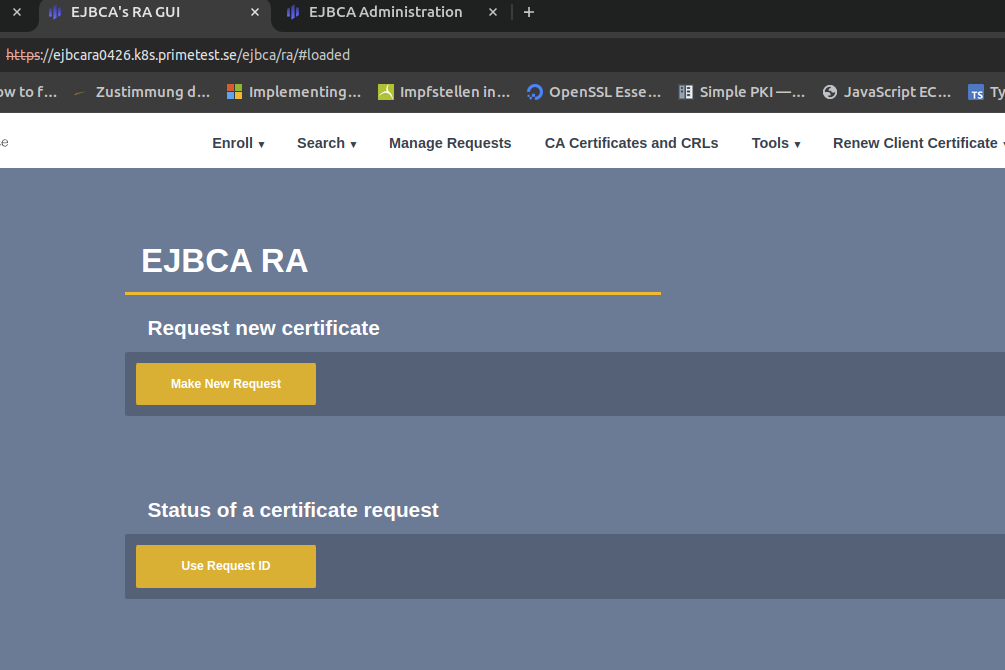
Verify VA
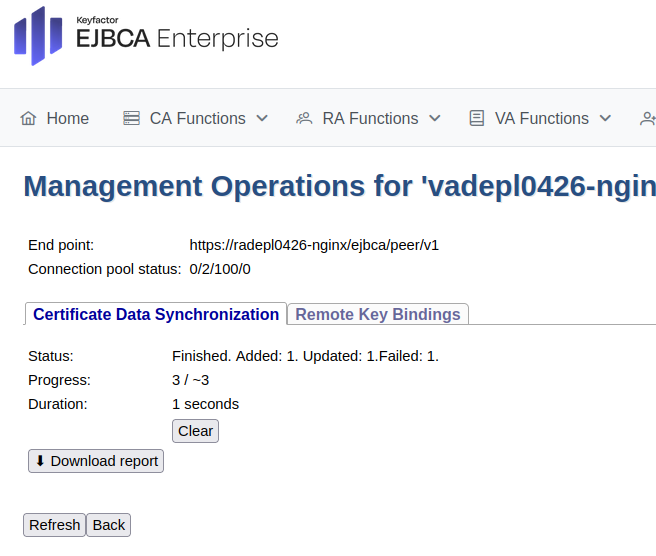
In EJBCA, click System Functions>Peer Systems.
Click Manage for the peer connector representing the VA.
Select the Certificate Data Synchronization tab.
Click Start to initiate the synchronization and follow the process.
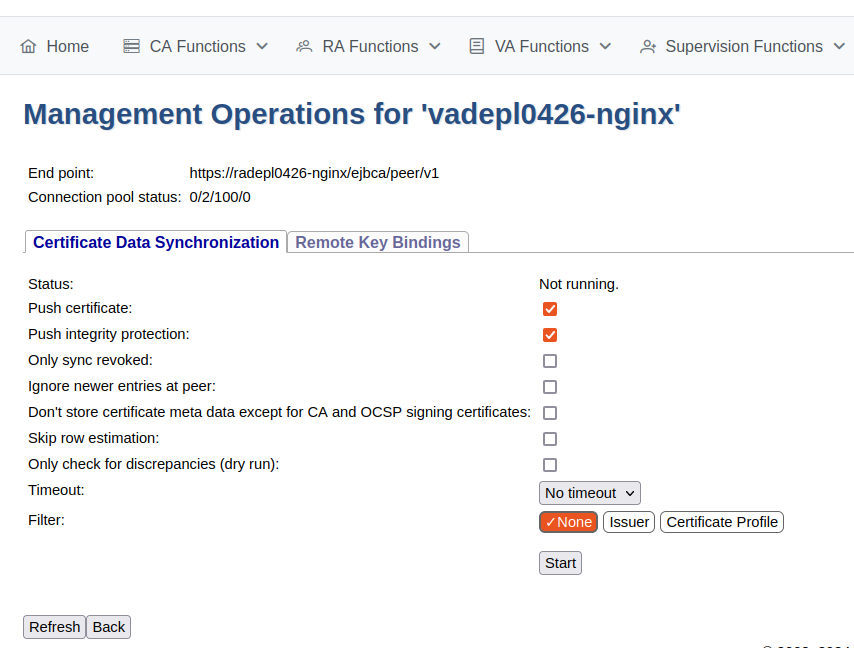
Click Refresh to display status information similar to the following.
Next Steps
This demonstrated how to deploy RA and VA instances using a LoadBalancer service. For alternative deployment options, see the following.
.png)