PKI for Kubernetes: Scalable Trust in Cloud-Native Environments
Securing Kubernetes requires more than TLS, it demands automated mTLS, workload identities, and centralized PKI that scales with cert-manager, service meshes, and multi-cluster environments. Learn how EJBCA PKI secures Kubernetes with secure identities, strong infrastructure protection, and compliance-ready trust across clusters and clouds.
In cloud-native environments, Kubernetes has become the de facto standard for orchestrating containerized workloads. However, securing these dynamic, distributed systems poses significant challenges. Engineers must ensure encrypted and authenticated service mesh communication, secure platform infrastructure, and automated certificate management at scale. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) provides the foundation for this trust when implemented correctly.
EJBCA PKI enables secure service mesh communication (e.g., Istio) and securing infrastructure components such as admission controllers, webhooks, and API servers.
This guide includes the following architectures with tutorials:
Automated Kubernetes Certificate Management with cert manager and EJBCA
Istio in a Multi Primary Multi Cluster Setup with EJBCA as External CA
TLS Everywhere: Certificates in Kubernetes
In Kubernetes, certificates secure nearly every layer, from cluster components and API endpoints to service-to-service communication. Workloads use mTLS certificates to achieve zero-trust service mesh communication, often via platforms like Istio or Linkerd. Ingress controllers and webhooks also rely on TLS certificates for secure connections. cert-manager has become a standard interface for managing certificates within Kubernetes clusters.
Avoiding Pitfalls in Kubernetes Certificate Management
Implementing PKI in Kubernetes isn’t just about enabling TLS, it is about doing it right. Certificates touch nearly every layer of the stack, and misconfigurations or inefficient solutions can quickly lead to outages or security gaps.
A certificate is more than just a file you attach to a service. Its security and trustworthiness come from how it’s issued, managed, and protected. Effective deployment requires skill in building a robust and effective PKI for this purpose.
Below are the key challenges to address to build a secure and reliable PKI foundation in the cluster:
Rotating certificates at short intervals across large, distributed clusters
Integrating external CA infrastructure with cloud-native tooling
Securing high-trust cryptographic operations in environments managed by infrastructure teams with broad access
Maintaining cryptographic agility and compliance readiness (e.g., post-quantum, HSM use, auditability)
Achieving compliance with regulations like NIS2, DORA, and the Cyber Resilience Act
EJBCA PKI is designed to work with Kubernetes-native patterns and tools to overcome these challenges, delivering scalable, compliant, and automated solutions.
Supported Architectures and Tutorials
EJBCA provides a Kubernetes-ready, enterprise-grade Certificate Authority with integrations for Kubernetes-native tools. It supports both ephemeral and persistent certificate lifecycles and is designed for high availability, cryptographic agility (including quantum-ready and hybrid cryptography), hardware security modules (HSMs), and resilient, scalable trust architectures.
Automated Kubernetes Certificate Management with cert-manager and EJBCA
Goal: Use EJBCA with cert-manager to issue X.509 certificates for Kubernetes and e.g. OpenShift, AKS, EKS, GKS and Tanzu workloads.
Key Steps:
Deploy cert-manager external issuer for EJBCA
Create RA role and profiles in EJBCA
Request certificates via cert-manager
Outcome: Automated TLS/mTLS management for Kubernetes-native workloads using a centralized, secure PKI.
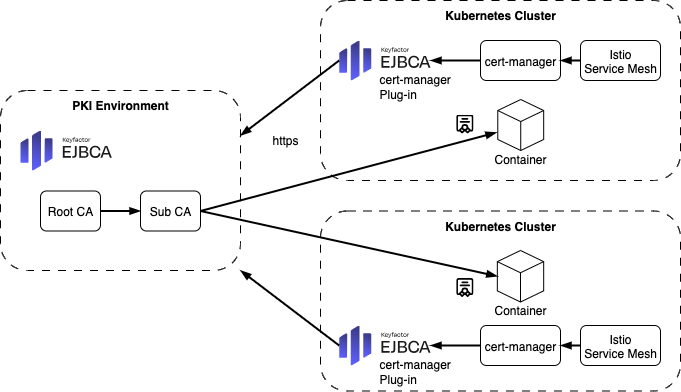
Istio Service Mesh mTLS with EJBCA and cert-manager
Goal: Automate mTLS certificate issuance for Istio and Ingress using EJBCA and cert-manager.
Key Steps:
Create certificate and end-entity profiles in EJBCA
Deploy cert-manager and istio-csr using Helm
Deploy Istio with a sample application
Outcome: Secure, automated service-to-service communication with scalable certificate management.
Read more: https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/deploy-istio-and-cert-manager-with-helm-to-issue-m
Istio in a Multi-Primary Multi-Cluster Setup with EJBCA as External CA
Each cluster runs its own Istiod and cert-manager instance.
cert-manager issues workload certificates signed by an intermediate CA.
All intermediate CAs are chained to the same EJBCA root, forming a shared trust domain.
Outcome: This setup enables secure cross-cluster communication in a multi-primary Istio deployment by aligning trust across environments.
Read more: https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/deploy-istio-service-mesh-in-a-multi-cluster-kuber
Integrating EJBCA with HashiCorp Vault
Goal: Use the ejbca-vault-pki-engine plugin to issue certificates from EJBCA via Vault.
Key Steps:
Configure EJBCA for the Vault plugin (profiles, RA certificate)
Deploy Vault in HA mode with the plugin enabled
Issue and manage certificates via Vault
Outcome: A unified, secure secrets and certificate management platform using EJBCA as a backend CA.
Read more: https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/use-ejbca-with-hashicorp-vault
Controlling Kubernetes Platform Security with Engineer Accountability
Problem
Kubernetes environments are often managed by teams of platform engineers with deep access to infrastructure. Without the right controls, visibility, and policy enforcement, there is a risk of accidental misconfigurations or insider threats compromising the platform’s security posture.
Solution
EJBCA provides centralized control over the issuance of credentials and signing authority. Multiple CAs, PKIs, and certificate types can be issued from the same platform. Engineers operate within defined roles, and all actions are logged and traceable.
Capabilities include:
Role-based access controls and audit trails for certificate and signing requests
Kubernetes-native automation with external approvers or security gate workflows
Dynamic deployment with automated install and config
Isolation of high-trust key material in HSMs (Hardware Security Module)
This helps maintain a balance between empowering engineers to move fast and maintaining a strong security baseline.
Conclusion
Securing Kubernetes environments involves more than basic TLS. It requires automated mTLS for service mesh communication, encrypted infrastructure components, and compliance-ready trust anchors across clusters and clouds. Many teams struggle to connect cloud-native tools like cert-manager and Istio with enterprise-grade PKI. This guide shows how to use EJBCA to unify Kubernetes-native automation with centralized governance, enabling secure, scalable certificate management and strong cryptographic assurance.
Related Content
Hands-On Guides:
https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/deploy-ejbca-using-a-helm-chart
https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/deploy-ejbca-enterprise-ca-with-helm-chart
https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/configure-ejbca-to-issue-short-lived-ephemeral-cer
https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/deploy-ejbca-container-in-microk8s
https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/deploy-ejbca-container-to-issue-certificates-to-an
https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/deploy-istio-and-cert-manager-with-helm-to-issue-m
https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/deploy-istio-service-mesh-in-a-multi-cluster-kuber
https://docs.keyfactor.com/how-to/latest/use-ejbca-with-hashicorp-vault
Contact us
Request a live demo with one of our experts — whether you want to explore workflows hands-on or discuss your specific needs.
.png)